Simultaneous central nervous system distribution and pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling of the electroencephalogram effect of norfloxacin administered at a convulsant dose in rats
- PMID: 15155539
- PMCID: PMC1574943
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705748
Simultaneous central nervous system distribution and pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling of the electroencephalogram effect of norfloxacin administered at a convulsant dose in rats
Abstract
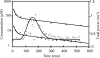
The objective of this study was to investigate the contribution of norfloxacin blood-brain barrier (BBB) transport to its delayed electroencephalogram (EEG) effect in rats. Norfloxacin was injected as a bolus dose of 150 mg kg(-1). Blood samples were collected for total norfloxacin plasma concentration measurements. The corresponding unbound levels were determined in brain extracellular fluid (ECF) using microdialysis. Quantitative EEG recording was conducted during 9 h post-dose. Brain ECF norfloxacin concentrations were much lower than plasma levels (AUC ratio=9.7+/-2.8%) but peaked very early, and concentration versus time profiles were parallel in both biological fluids. The best pharmacokinetic (PK) modelling was obtained by considering that ECF concentrations were part of the central compartment, with a proportionality factor. The peak of EEG effect was delayed and the effect versus plasma concentration curves exhibited a dramatic hysteresis. A PK-pharmacodynamic (PD) effect compartment model with a spline function to describe the relationship between effect and concentration at the effect site successfully described the data. Comparisons of PK-PD parameters estimated from plasma and ECF concentrations show that most of the delayed norfloxacin EEG effect is not due to BBB transport, but also that PD parameters derived from plasma data must be carefully interpreted when drug distribution at the effect site is restricted, as may often be the case for centrally acting drugs.
Figures


References
-
- BERGMAN I., BURCKART G.J., POHL C.R., VENKATARAMANAM R., BARMADA M.A., GRIFFIN J.A., HEUNG N.-K.V. Pharmacokinetics of IgG and IgM anti-ganglioside antibodies in rats and monkeys after intrathecal administration. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap. 1998;284:111–115. - PubMed
-
- BOUW R., GARDMARK M., HAMMARLUND-UDENAES M. Pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic modelling of morphine transport across the blood–brain barrier as a cause of the antinociceptive effect delay in rats – a microdialysis study. Pharm. Res. 2000;17:1220–1227. - PubMed
-
- DE LANGE E., MARCHAND S., VAN DEN BERG D.-J., VAN DER SANDT I.C.J., DE BOER A.G., DELON A., BOUQUET S, COUET W. In vitro and in vivo investigations on fluoroquinolones; effects of the P-glycoprotein efflux transporter on brain distribution of sparfloxacin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000;12:85–93. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

