Snail blocks the cell cycle and confers resistance to cell death
- PMID: 15155580
- PMCID: PMC415638
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.294104
Snail blocks the cell cycle and confers resistance to cell death
Abstract
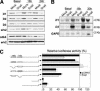
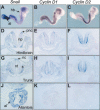
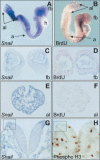
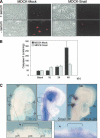
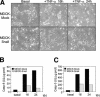
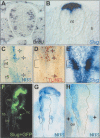
The Snail zinc-finger transcription factors trigger epithelial-mesenchymal transitions (EMTs), endowing epithelial cells with migratory and invasive properties during both embryonic development and tumor progression. During EMT, Snail provokes the loss of epithelial markers, as well as changes in cell shape and the expression of mesenchymal markers. Here, we show that in addition to inducing dramatic phenotypic alterations, Snail attenuates the cell cycle and confers resistance to cell death induced by the withdrawal of survival factors and by pro-apoptotic signals. Hence, Snail favors changes in cell shape versus cell division, indicating that with respect to oncogenesis, although a deregulation/increase in proliferation is crucial for tumor formation and growth, this may not be so for tumor malignization. Finally, the resistance to cell death conferred by Snail provides a selective advantage to embryonic cells to migrate and colonize distant territories, and to malignant cells to separate from the primary tumor, invade, and form metastasis.
Figures



References
-
- Aybar M., Nieto, M.A., and Mayor, R. 2003. Snail precedes Slug in the genetic cascade required for the specification and migration of the Xenopus neural crest. Development 130: 483–494. - PubMed
-
- Batlle E., Sancho, E., Franci, C., Dominguez, D., Monfar, M., Baulida, J., and Garcia De Herreros, A. 2000. The transcription factor Snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumor cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2: 84–89. - PubMed
-
- Blanco M.J., Moreno-Bueno, G., Sarrio, D., Locascio, A., Cano, A., Palacios, J., and Nieto, M.A. 2002. Correlation of Snail expression with histological grade and lymph node status in breast carcinomas. Oncogene 21: 3241–3246. - PubMed
-
- Bonneton C., Sibarita, J.-B., and Thiery, J.P. 1999. Relationship between cell migration and cell cycle during the initiation of epithelial to fibroblastoid transition. Cell Mot. Cytosk. 43: 288–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
