New synaptic bouton formation is disrupted by misregulation of microtubule stability in aPKC mutants
- PMID: 15157419
- PMCID: PMC4656022
- DOI: 10.1016/s0896-6273(04)00255-7
New synaptic bouton formation is disrupted by misregulation of microtubule stability in aPKC mutants
Abstract
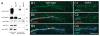
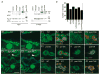
The Baz/Par-3-Par-6-aPKC complex is an evolutionarily conserved cassette critical for the development of polarity in epithelial cells, neuroblasts, and oocytes. aPKC is also implicated in long-term synaptic plasticity in mammals and the persistence of memory in flies, suggesting a synaptic function for this cassette. Here we show that at Drosophila glutamatergic synapses, aPKC controls the formation and structure of synapses by regulating microtubule (MT) dynamics. At the presynapse, aPKC regulates the stability of MTs by promoting the association of the MAP1Brelated protein Futsch to MTs. At the postsynapse, aPKC regulates the synaptic cytoskeleton by controlling the extent of Actin-rich and MT-rich areas. In addition, we show that Baz and Par-6 are also expressed at synapses and that their synaptic localization depends on aPKC activity. Our findings establish a novel role for this complex during synapse development and provide a cellular context for understanding the role of aPKC in synaptic plasticity and memory.
Figures






References
-
- Banan A, Zhang L, Fields JZ, Farhadi A, Talmage DA, Keshavarzian A. PKC-zeta prevents oxidant-induced iNOS upregulation and protects the microtubules and gut barrier integrity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002;283:G909–G922. - PubMed
-
- Brand AH, Perrimon N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 1993;118:401–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

