Programmable cells: interfacing natural and engineered gene networks
- PMID: 15159530
- PMCID: PMC420408
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0402940101
Programmable cells: interfacing natural and engineered gene networks
Abstract
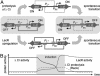
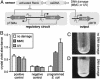
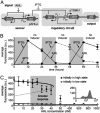
Novel cellular behaviors and characteristics can be obtained by coupling engineered gene networks to the cell's natural regulatory circuitry through appropriately designed input and output interfaces. Here, we demonstrate how an engineered genetic circuit can be used to construct cells that respond to biological signals in a predetermined and programmable fashion. We employ a modular design strategy to create Escherichia coli strains where a genetic toggle switch is interfaced with: (i) the SOS signaling pathway responding to DNA damage, and (ii) a transgenic quorum sensing signaling pathway from Vibrio fischeri. The genetic toggle switch endows these strains with binary response dynamics and an epigenetic inheritance that supports a persistent phenotypic alteration in response to transient signals. These features are exploited to engineer cells that form biofilms in response to DNA-damaging agents and cells that activate protein synthesis when the cell population reaches a critical density. Our work represents a step toward the development of "plug-and-play" genetic circuitry that can be used to create cells with programmable behaviors.
Figures



References
-
- Benner, S. A. (2003) Nature 421, 118. - PubMed
-
- Ferber, D. (2004) Science 303, 158-161. - PubMed
-
- Elowitz, M. B. & Leibler, S. (2000) Nature 403, 335-338. - PubMed
-
- Gardner, T. S., Cantor, C. R. & Collins, J. J. (2000) Nature 403, 339-342. - PubMed
-
- Tchuraev, R. N., Stupak, I. V., Tropynina, T. S. & Stupak, E. E. (2000) FEBS Lett. 486, 200-202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

