Response properties of whisker-related neurons in rat second somatosensory cortex
- PMID: 15163670
- PMCID: PMC2804247
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00262.2004
Response properties of whisker-related neurons in rat second somatosensory cortex
Abstract
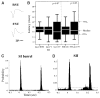
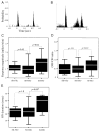
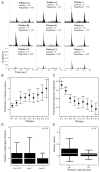
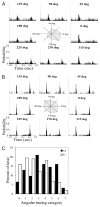
In addition to a primary somatosensory cortex (SI), the cerebral cortex of all mammals contains a second somatosensory area (SII); however, the functions of SII are largely unknown. Our aim was to explore the functions of SII by comparing response properties of whisker-related neurons in this area with their counterparts in the SI. We obtained extracellular unit recordings from narcotized rats, in response to whisker deflections evoked by a piezoelectric device, and compared response properties of SI barrel (layer IV) neurons with those of SII (layers II to VI) neurons. Neurons in both cortical areas have similar response latencies and spontaneous activity levels. However, SI and SII neurons differ in several significant properties. The receptive fields of SII neurons are at least five times as large as those of barrel neurons, and they respond equally strongly to several principal whiskers. The response magnitude of SII neurons is significantly smaller than that of neurons in SI, and SII neurons are more selective for the angle of whisker deflection. Furthermore, whereas in SI fast-spiking (inhibitory) and regular-spiking (excitatory) units have different spontaneous and evoked activity levels and differ in their responses to stimulus onset and offset, SII neurons do not show significant differences in these properties. The response properties of SII neurons suggest that they are driven by thalamic inputs that are part of the paralemniscal system. Thus whisker-related inputs are processed in parallel by a lemniscal system involving SI and a paralemniscal system that processes complimentary aspects of somatosensation.
Figures
References
-
- Alloway KD, Burton H. Homotypical ipsilateral cortical projections between somatosensory areas I and II in the cat. Neuroscience. 1985a;14:15–35. - PubMed
-
- Alloway KD, Burton H. Submodality and columnar organization of the second somatic sensory area in cats. Exp Brain Res. 1985b;61:128–140. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong-James M. The nature and plasticity of sensory processing within adult rat barrel cortex. In: Jones EG, Diamond IT, editors. Cerebral Cortex: The Barrel Cortex of Rodents. Vol. 11. New York: Plenum Press; 1995. pp. 333–373.
-
- Armstrong-James M, Fox K, Dasgupta A. Flow of excitation within rat barrel cortex on striking a single vibrissa. J Neurophysiol. 1992;68:1345–1358. - PubMed
-
- Brumberg JC, Pinto DJ, Simons DJ. Cortical columnar processing in the rat whisker-to-barrel system. J Neurophysiol. 1999;82:1808–1817. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

