Firing mode-dependent synaptic plasticity in rat neocortical pyramidal neurons
- PMID: 15163685
- PMCID: PMC6729368
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0795-04.2004
Firing mode-dependent synaptic plasticity in rat neocortical pyramidal neurons
Abstract
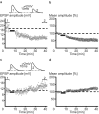
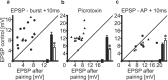
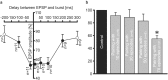
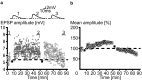
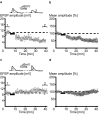
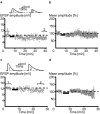
Pyramidal cells in the mammalian neocortex can emit action potentials either as series of individual spikes or as distinct clusters of high-frequency bursts. However, why two different firing modes exist is largely unknown. In this study, we report that in layer V pyramidal cells of the rat somatosensory cortex, in vitro associations of EPSPs with spike bursts delayed by +10 msec led to long-term synaptic depression (LTD), whereas pairings with individual action potentials at the same delay induced long-term potentiation. EPSPs were evoked extracellularly in layer II-III and recorded intracellularly in layer V neurons with the whole-cell or nystatin-based perforated patch-clamp technique. Bursts were evoked with brief somatic current injections, resulting in three to four action potentials with interspike frequencies of approximately 200 Hz, characteristic of intrinsic burst firing. Burst-firing-associated LTD (Burst-LTD) was robust over a wide range of intervals between -100 and +200 msec, and depression was maximal (approximately 50%) for closely spaced presynaptic and postsynaptic events. Burst-LTD was associative and required concomitant activation of low voltage-activated calcium currents and metabotropic glutamate receptors. Conversely, burst-LTD was resistant to blockade of NMDA receptors or inhibitory synaptic potentials. Burst-LTD was also inducible at already potentiated synapses. We conclude that intrinsic burst firing represents a signal for resetting excitatory synaptic weights.
Figures


References
-
- Abbott LF, Nelson SB (2000) Synaptic plasticity: taming the beast. Nat Neurosci 3: 1178-1183. - PubMed
-
- Akaike N, Hattori K, Oomura Y, Carpenter DO (1985) Bicuculline and picrotoxin block gamma-aminobutyric acid-gated Cl- conductance by different mechanisms. Experientia 41: 70-71. - PubMed
-
- Bear MF, Press WA, Connors BW (1992) Long-term potentiation in slices of kitten visual cortex and the effects of NMDA receptor blockade. J Neurophysiol 67: 841-851. - PubMed
-
- Braunewell KH, Manahan-Vaughan D (2001) Long-term depression: a cellular basis for learning? Rev Neurosci 12: 121-140. - PubMed
-
- Connors BW, Gutnick MJ, Prince DA (1982) Electrophysiological properties of neocortical neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol 48: 1302-1320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
