Dynamic interactions between 14-3-3 proteins and phosphoproteins regulate diverse cellular processes
- PMID: 15167810
- PMCID: PMC1133837
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20031332
Dynamic interactions between 14-3-3 proteins and phosphoproteins regulate diverse cellular processes
Abstract
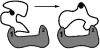
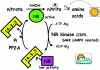
14-3-3 proteins exert an extraordinarily widespread influence on cellular processes in all eukaryotes. They operate by binding to specific phosphorylated sites on diverse target proteins, thereby forcing conformational changes or influencing interactions between their targets and other molecules. In these ways, 14-3-3s 'finish the job' when phosphorylation alone lacks the power to drive changes in the activities of intracellular proteins. By interacting dynamically with phosphorylated proteins, 14-3-3s often trigger events that promote cell survival--in situations from preventing metabolic imbalances caused by sudden darkness in leaves to mammalian cell-survival responses to growth factors. Recent work linking specific 14-3-3 isoforms to genetic disorders and cancers, and the cellular effects of 14-3-3 agonists and antagonists, indicate that the cellular complement of 14-3-3 proteins may integrate the specificity and strength of signalling through to different cellular responses.
Figures



References
-
- Johnson L. N., Barford D. The effects of phosphorylation on the structure and function of proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1993;22:199–232. - PubMed
-
- Hubbard M. J., Cohen P. On target with a new mechanism of protein phosphorylation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1993;18:172–177. - PubMed
-
- Pawson T., Scott J. D. Signaling through scaffold, anchoring, and adaptor proteins. Science. 1997;278:2075–2080. - PubMed
-
- Pawson T., Raina M., Nash P. Interaction domains: from simple binding events to complex cellular behavior. FEBS Lett. 2002;513:2–10. - PubMed
-
- Bradshaw J. M., Waksman G. Molecular recognition by SH2 domains. Adv. Protein Chem. 2002;61:161–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

