Molecular determinants of differential pore blocking of kidney CLC-K chloride channels
- PMID: 15167890
- PMCID: PMC1299079
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400169
Molecular determinants of differential pore blocking of kidney CLC-K chloride channels
Abstract
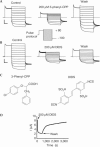
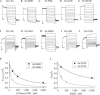
The highly homologous Cl(-) channels CLC-Ka and CLC-Kb are important for water and salt conservation in the kidney and for the production of endolymph in the inner ear. Mutations in CLC-Kb lead to Bartter's syndrome and mutations in the small CLC-K subunit barttin lead to Bartter's syndrome and deafness. Here we show that CLC-Ka is blocked by the recently identified blocker 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)-3-phenylpropionic acid of the rat channel CLC-K1 with an apparent K(D) approximately 80 microM. We also found that DIDS (4,4'-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2'-disulphonic acid), a generic Cl(-) channel blocker, inhibits CLC-Ka (K(D) approximately 90 microM). Surprisingly, the highly homologous channel CLC-Kb is fivefold to sixfold less sensitive to both compounds. Guided by the crystal structure of bacterial CLC proteins, we identify two amino acids, N68/D68 and G72/E72, in CLC-Ka and CLC-Kb, respectively, that are responsible for the differential drug sensitivity. Both residues expose their side chains in the extracellular pore mouth, delineating the probable drug binding site. These novel CLC-K channel blockers are promising lead compounds for the development of new diuretic drugs.
Figures



Comment in
-
CLC-K channels: if the drug fits, use it.EMBO Rep. 2004 Jun;5(6):565-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400168. EMBO Rep. 2004. PMID: 15170474 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
New light on the "old" chloride channel blocker DIDS.ACS Chem Biol. 2008 Jul 18;3(7):399-401. doi: 10.1021/cb800140m. ACS Chem Biol. 2008. PMID: 18642798
-
Molecular requisites for drug binding to muscle CLC-1 and renal CLC-K channel revealed by the use of phenoxy-alkyl derivatives of 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)propionic acid.Mol Pharmacol. 2002 Aug;62(2):265-71. doi: 10.1124/mol.62.2.265. Mol Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12130677
-
Investigations of pharmacologic properties of the renal CLC-K1 chloride channel co-expressed with barttin by the use of 2-(p-Chlorophenoxy)propionic acid derivatives and other structurally unrelated chloride channels blockers.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004 Jan;15(1):13-20. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000103226.28798.ea. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004. PMID: 14694153
-
CLC-K channels: if the drug fits, use it.EMBO Rep. 2004 Jun;5(6):565-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400168. EMBO Rep. 2004. PMID: 15170474 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Channel or transporter? The CLC saga continues.Exp Physiol. 2006 Jan;91(1):149-52. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2005.031799. Epub 2005 Sep 22. Exp Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16179405 Review.
Cited by
-
Chloride channels as drug targets.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009 Feb;8(2):153-71. doi: 10.1038/nrd2780. Epub 2008 Jan 19. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009. PMID: 19153558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of transmembrane member 16A calcium-activated chloride channels by natural flavonoids contributes to flavonoid anticancer effects.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Jul;174(14):2334-2345. doi: 10.1111/bph.13841. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28452066 Free PMC article.
-
I-J loop involvement in the pharmacological profile of CLC-K channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Nov;1838(11):2745-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.07.021. Epub 2014 Jul 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 25073071 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory-auxiliary subunits of CLC chloride channel-transport proteins.J Physiol. 2015 Sep 15;593(18):4111-27. doi: 10.1113/JP270057. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25762128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual regulation of the native ClC-K2 chloride channel in the distal nephron by voltage and pH.J Gen Physiol. 2016 Sep;148(3):213-26. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201611623. J Gen Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27574292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi S, Uchida S, Ito H, Hata M, Hiroe M, Marumo F, Sasaki S (1994) Two isoforms of a chloride channel predominantly expressed in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop and collecting ducts of rat kidney. J Biol Chem 269: 17677–17683 - PubMed
-
- Bartel D, Hans H, Passow H (1989) Identification by site-directed mutagenesis of Lys-558 as the covalent attachment site of H2DIDS in the mouse erythroid band 3 protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 985: 355–358 - PubMed
-
- Birkenhäger R et al. (2001) Mutation of BSND causes Bartter syndrome with sensorineural deafness and kidney failure. Nat Genet 29: 310–314 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

