Age-related maculopathy: a genomewide scan with continued evidence of susceptibility loci within the 1q31, 10q26, and 17q25 regions
- PMID: 15168325
- PMCID: PMC1216053
- DOI: 10.1086/422476
Age-related maculopathy: a genomewide scan with continued evidence of susceptibility loci within the 1q31, 10q26, and 17q25 regions
Abstract
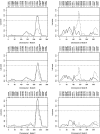
Age-related maculopathy (ARM), or age-related macular degeneration, is one of the most common causes of visual impairment in the elderly population of developed nations. In a combined analysis of two previous genomewide scans that included 391 families, containing up to 452 affected sib pairs, we found linkage evidence in four regions: 1q31, 9p13, 10q26, and 17q25. We now have added a third set of families and have performed an integrated analysis incorporating 530 families and up to 736 affected sib pairs. Under three diagnostic models, we have conducted linkage analyses using parametric (heterogeneity LOD [HLOD] scores under an autosomal dominant model) and nonparametric (Sall statistic) methods. There is ongoing evidence of susceptibility loci within the 1q31, 10q26, and 17q25 regions. If we treat the third set of families as a replication set, then two regions (10q26 and 17q25) are replicated, with LOD scores >1.0. If we pool all our data together, then four regions (1q31, 2q14.3, 10q26, and 17q25) show HLOD or Sall scores > or =2.0. Within the 1q31 region, we observed an HLOD of 2.72 (genomewide P=.061) under our least stringent diagnostic model, whereas the 17q25 region contained a maximal HLOD of 3.53 (genomewide P=.007) under our intermediate diagnostic model. We have evaluated our results with respect to the findings from several new independent genomewide linkage studies and also have completed ordered subset analyses (OSAs) with apolipoprotein E alleles, smoking history, and age at onset as stratifying covariates. The OSAs generate the interesting hypothesis that the effect of smoking on the risk of ARM is accentuated by a gene in the 10q26 region--a region implicated by four other studies.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/
References
-
- Abecasis GR, Yashar BM, Zhao Y, Ghiasvand N, Zareparsi S, Branham KEH, Reddick AC, Trager EH, Yoshida S, Bahling J, Filippova E, Elner S, Johnson MW, Vine AK, Sieving PA, Jacobson SG, Richards JE, Swaroop A (2004) Agerelated macular degeneration: a high resolution genome scan for susceptibility loci in a population enriched for late-stage disease. Am J Hum Genet 74:482–494 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bonastre J, Le Pen C, Soubrane G, Quentel G (2003) The burden of age-related macular degeneration: results of a cohort study in two French referral centres. Pharmacoeconomics 21:181–190 - PubMed
-
- Breitner JC, Jarvik GP, Plassman BL, Saunders AM, Welsh KA (1998) Risk of Alzheimer disease with the epsilon4 allele for apolipoprotein E in a population-based study of men aged 62–73 years. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 12:40–44 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

