Diffuse scattering provides material parameters and electron density profiles of biomembranes
- PMID: 15169001
- PMCID: PMC2761748
- DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.69.040901
Diffuse scattering provides material parameters and electron density profiles of biomembranes
Abstract
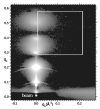
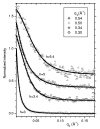
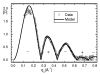
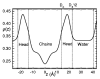
Fully hydrated stacks of DOPC lipid bilayer membranes generate large diffuse x-ray scattering that corrupts the Bragg peak intensities that are used in conventional biophysical structural analysis, but the diffuse scattering actually contains more information. Using an efficient algorithm for fitting extensive regions of diffuse data to classical smectic liquid crystalline theory we first obtain the compressional modulus B= 10(13) erg/ cm(4), which involves interactions between membranes, and the bending modulus K(c) =8x 10(-13) erg of the membranes. The membrane form factor F ( q(z) ) is then obtained for most values of q(z) up to 0.8 A(-1). The electron density profile rho(z) is obtained by fitting models to F( q(z) ). Constraining the models to conform to other measurements provides structural quantities such as area A=72.1+/-0.5 A(2) per lipid at the interface.
Figures
References
-
- Caillé A. C. R. Acad. Sc. Paris: Ser. B. 1972;274:891.
-
- Als-Nielsen J, Litster JD, Birgeneau RJ, Kaplan M, Safinya CR, Lindegaard-Andersen A, Mathiesen S. Phys. Rev. B. 1980;22:312.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
