Short-lived plasmablasts and long-lived plasma cells contribute to chronic humoral autoimmunity in NZB/W mice
- PMID: 15173206
- PMCID: PMC2211779
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20040168
Short-lived plasmablasts and long-lived plasma cells contribute to chronic humoral autoimmunity in NZB/W mice
Abstract
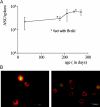
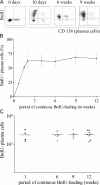
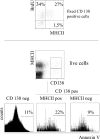
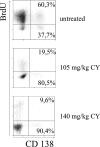
The current view holds that chronic autoimmune diseases are driven by the continuous activation of autoreactive B and T lymphocytes. However, despite the use of potent immunosuppressive drugs designed to interfere with this activation the production of autoantibodies often persists and contributes to progression of the immunopathology. In the present study, we analyzed the life span of (auto)antibody-secreting cells in the spleens of NZB x NZW F1 (NZB/W) mice, a murine model of systemic lupus erythematosus. The number of splenic ASCs increased in mice aged 1-5 mo and became stable thereafter. Less than 60% of the splenic (auto)antibody-secreting cells were short-lived plasmablasts, whereas 40% were nondividing, long-lived plasma cells with a half-life of >6 mo. In NZB/W mice and D42 Ig heavy chain knock-in mice, a fraction of DNA-specific plasma cells were also long-lived. Although antiproliferative immunosuppressive therapy depleted short-lived plasmablasts, long-lived plasma cells survived and continued to produce (auto)antibodies. Thus, long-lived, autoreactive plasma cells are a relevant target for researchers aiming to develop curative therapies for autoimmune diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Tan, E.M. 1991. Autoantibodies in pathology and cell biology. Cell. 67:841–842. - PubMed
-
- Ji, H., A.S. Korganow, S. Mangialaio, P. Hoglund, I. Andre, F. Luhder, A. Gonzalez, L. Poirot, C. Benoist, and D. Mathis. 1999. Different modes of pathogenesis in T-cell-dependent autoimmunity: clues from two TCR transgenic systems. Immunol. Rev. 169:139–146. - PubMed
-
- Hahn, B.H. 1998. Antibodies to DNA. N. Engl. J. Med. 338:1359–1368. - PubMed
-
- Lipsky, P.E. 2001. Systemic lupus erythematosus: an autoimmune disease of B cell hyperactivity. Nat. Immunol. 2:764–766. - PubMed
-
- Duke-Cohan, J.S., A. Rubinow, R. Hirt, and D. Naor. 1990. The reaction against autologous lymphoblasts as an indicator of lymphocyte hyperreactivity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 54:298–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

