Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta mediates convergence of protection signaling to inhibit the mitochondrial permeability transition pore
- PMID: 15173880
- PMCID: PMC419483
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI19906
Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta mediates convergence of protection signaling to inhibit the mitochondrial permeability transition pore
Abstract
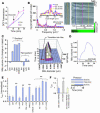
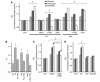
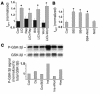
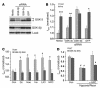
Environmental stresses converge on the mitochondria that can trigger or inhibit cell death. Excitable, postmitotic cells, in response to sublethal noxious stress, engage mechanisms that afford protection from subsequent insults. We show that reoxygenation after prolonged hypoxia reduces the reactive oxygen species (ROS) threshold for the mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) in cardiomyocytes and that cell survival is steeply negatively correlated with the fraction of depolarized mitochondria. Cell protection that exhibits a memory (preconditioning) results from triggered mitochondrial swelling that causes enhanced substrate oxidation and ROS production, leading to redox activation of PKC, which inhibits glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta). Alternatively, receptor tyrosine kinase or certain G protein-coupled receptor activation elicits cell protection (without mitochondrial swelling or durable memory) by inhibiting GSK-3beta, via protein kinase B/Akt and mTOR/p70(s6k) pathways, PKC pathways, or protein kinase A pathways. The convergence of these pathways via inhibition of GSK-3beta on the end effector, the permeability transition pore complex, to limit MPT induction is the general mechanism of cardiomyocyte protection.
Figures





Comment in
-
Inhibit GSK-3beta or there's heartbreak dead ahead.J Clin Invest. 2004 Jun;113(11):1526-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI21986. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15173876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Green DR, Reed JC. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science. 1998;281:1309–1312. - PubMed
-
- Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986;74:1124–1136. - PubMed
-
- Kloner RA, Bolli R, Marban E, Reinlib L, Braunwald E. Medical and cellular implications of stunning, hibernation, and preconditioning: an NHLBI workshop. Circulation. 1998;97:1848–1867. - PubMed
-
- Inoue I, Nagase H, Kishi K, Higuti T. ATP-sensitive K+ channel in the mitochondrial inner membrane. Nature. 1991;352:244–247. - PubMed
-
- Garlid KD, et al. Cardioprotective effect of diazoxide and its interaction with mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Possible mechanism of cardioprotection. Circ. Res. 1997;81:1072–1082. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

