Differential expression of 5HT-1A, alpha 1b adrenergic, CRF-R1, and CRF-R2 receptor mRNA in serotonergic, gamma-aminobutyric acidergic, and catecholaminergic cells of the rat dorsal raphe nucleus
- PMID: 15174080
- PMCID: PMC2430888
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.20138
Differential expression of 5HT-1A, alpha 1b adrenergic, CRF-R1, and CRF-R2 receptor mRNA in serotonergic, gamma-aminobutyric acidergic, and catecholaminergic cells of the rat dorsal raphe nucleus
Abstract
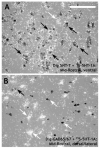
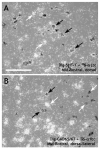
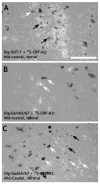
The dorsal raphe nucleus (DR) has a topographic neuroanatomy consistent with the idea that different parts of this nucleus subserve different functions. Here we use dual in situ hybridization to describe the rostral-caudal neurochemical distribution of three major cell groups, serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT), gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and catecholamine, and their relative colocalization with each other and mRNA encoding four different receptor subtypes that have been described to influence DR responses, namely, 5HT-1A, alpha(1b) adrenergic (alpha(1b) ADR), and corticotropin-releasing factor type 1 (CRF-R1) and 2 (CRF-R2) receptors. Serotonergic and GABAergic neurons were distributed throughout the rostral-caudal extent of the DR, whereas catecholaminergic neurons were generally restricted to the rostral half of the nucleus. These phenotypes essentially represent distinct cell populations, because the neurochemical markers were rarely colocalized. Both 5HT-1A and alpha(1b) ADR mRNA were highly expressed throughout the DR, and the vast majority of serotonergic neurons expressed both receptors. A smaller percentage of GABAergic neurons also expressed 5HT-1A or alpha(1b) ADR mRNA. Very few catecholaminergic cells expressed either 5HT-1A or alpha(1b) ADR mRNA. CRF-R1 mRNA was detected only at very low levels within the DR, and quantitative colocalization studies were not technically feasible. CRF-R2 mRNA was mainly expressed at the middle and caudal levels of the DR. At midlevels, CRF-R2 mRNA was expressed exclusively in serotonin neurons, whereas, at caudal levels, approximately half the CRF-R2 mRNA was expressed in GABAergic neurons. The differential distribution of distinct neurochemical phenotypes lends support to the idea of functional differentiation of the DR.
Copyright 2004 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


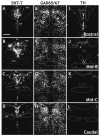
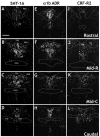
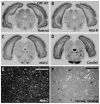
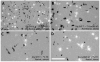
Similar articles
-
Corticotropin-releasing factor increases GABA synaptic activity and induces inward current in 5-hydroxytryptamine dorsal raphe neurons.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 26;28(48):12927-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2887-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19036986 Free PMC article.
-
Wheel running alters serotonin (5-HT) transporter, 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, and alpha 1b-adrenergic receptor mRNA in the rat raphe nuclei.Biol Psychiatry. 2005 Mar 1;57(5):559-68. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.11.025. Biol Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15737672
-
Inhibition of serotonin outflow by nociceptin/orphaninFQ in dorsal raphe nucleus slices from normal and stressed rats: Role of corticotropin releasing factor.Neurochem Int. 2009 May-Jun;54(5-6):378-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2009.01.004. Neurochem Int. 2009. PMID: 19418633
-
The structure of the dorsal raphe nucleus and its relevance to the regulation of sleep and wakefulness.Sleep Med Rev. 2010 Oct;14(5):307-17. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2009.11.004. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Sleep Med Rev. 2010. PMID: 20153669 Review.
-
Effects of citalopram on serotonin and CRF systems in the midbrain of primates with differences in stress sensitivity.J Chem Neuroanat. 2011 Jul;41(4):200-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2011.05.010. Epub 2011 Jun 6. J Chem Neuroanat. 2011. PMID: 21683135 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A subpopulation of serotonergic neurons that do not express the 5-HT1A autoreceptor.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Jan 16;4(1):89-95. doi: 10.1021/cn300157s. Epub 2012 Nov 7. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23336048 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in anxiety and emotional behavior.Pflugers Arch. 2013 May;465(5):601-26. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1271-7. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Pflugers Arch. 2013. PMID: 23588380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic amphetamine treatment enhances corticotropin-releasing factor-induced serotonin release in the amygdala.Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Oct 10;644(1-3):80-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.07.008. Epub 2010 Jul 23. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20655906 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of genetic and pharmacological blockade of GABA receptors on the 5-HT2C receptor function during stress.J Neurochem. 2014 Dec;131(5):566-72. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12929. Epub 2014 Sep 4. J Neurochem. 2014. PMID: 25113583 Free PMC article.
-
Somatosensory regulation of serotonin release in the central nucleus of the amygdala is mediated via corticotropin releasing factor and gamma-aminobutyric acid in the dorsal raphe nucleus.J Physiol Sci. 2017 Nov;67(6):689-698. doi: 10.1007/s12576-016-0498-4. Epub 2016 Oct 15. J Physiol Sci. 2017. PMID: 27744641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baraban JM, Aghajanian GK. Suppression of firing activity of 5-HT neurons in the dorsal raphe by alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology. 1980a;19:355–363. - PubMed
-
- Baraban JM, Aghajanian GK. Suppression of serotonergic neuronal firing by alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists: evidence against GABA mediation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980b;66:287–294. - PubMed
-
- Baraban JM, Aghajanian GK. Noradrenergic innervation of serotonergic neurons in the dorsal raphe: demonstration by electron microscopic autoradiography. Brain Res. 1981;204:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Belin MF, Nanopoulos D, Didier M, Aguera M, Steinbusch H, Verhofstad A, Maitre M, Pujol JF. Immunohistochemical evidence for the presence of gamma-aminobutyric acid and serotonin in one nerve cell. A study on the raphe nuclei of the rat using antibodies to glutamate decarboxylase and serotonin. Brain Res. 1983;275:329–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

