Repression of the Arf tumor suppressor by E2F3 is required for normal cell cycle kinetics
- PMID: 15175242
- PMCID: PMC423192
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1196704
Repression of the Arf tumor suppressor by E2F3 is required for normal cell cycle kinetics
Abstract
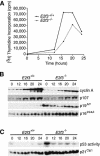
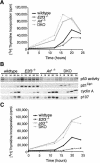
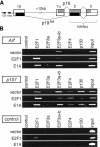
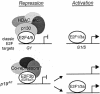
Tumor development is dependent upon the inactivation of two key tumor-suppressor networks, p16(Ink4a)-cycD/cdk4-pRB-E2F and p19(Arf)-mdm2-p53, that regulate cellular proliferation and the tumor surveillance response. These networks are known to intersect with one another, but the mechanisms are poorly understood. Here, we show that E2F directly participates in the transcriptional control of Arf in both normal and transformed cells. This occurs in a manner that is significantly different from the regulation of classic E2F-responsive targets. In wild-type mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), the Arf promoter is occupied by E2F3 and not other E2F family members. In quiescent cells, this role is largely fulfilled by E2F3b, an E2F3 isoform whose function was previously undetermined. E2f3 loss is sufficient to derepress Arf, triggering activation of p53 and expression of p21(Cip1). Thus, E2F3 is a key repressor of the p19(Arf)-p53 pathway in normal cells. Consistent with this notion, Arf mutation suppresses the activation of p53 and p21(Cip1) in E2f3-deficient MEFs. Arf loss also rescues the known cell cycle re-entry defect of E2f3(-/-) cells, and this correlates with restoration of appropriate activation of classic E2F-responsive genes. Our data also demonstrate a direct role for E2F in the oncogenic activation of Arf. Specifically, we observe recruitment of the endogenous activating E2Fs, E2F1, and E2F3a, to the Arf promoter. Thus, distinct E2F complexes directly contribute to the normal repression and oncogenic activation of Arf. We propose that monitoring of E2F levels and/or activity is a key component of Arf's ability to respond to inappropriate, but not normal cellular proliferation.
Figures

References
-
- Bates S., Phillips, A.C., Clark, P.A., Stott, F., Peters, G., Ludwig, R.L., and Vousden, K.H. 1998. p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature 395: 124-125. - PubMed
-
- Baudino T.A., Maclean, K.H., Brennan, J., Parganas, E., Yang, C., Aslanian, A., Lees, J.A., Sherr, C.J., Roussel, M.F., and Cleveland, J.L. 2003. Myc-mediated proliferation and lymphomagenesis, but not apoptosis, are compromised by E2f1 loss. Mol. Cell 11: 905-914. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Israel H. and Kleinberger, T. 2002. Adenovirus and cell cycle control. Front. Biosci. 7: d1369-d1395. - PubMed
-
- Berkovich E., Lamed, Y., and Ginsberg, D. 2003. E2F and Ras synergize in transcriptionally activating p14ARF expression. Cell Cycle 2: 127-133. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp T.R., Kortlever, R.M., Lingbeek, M., Trettel, F., MacDonald, M.E., van Lohuizen, M., and Bernards, R. 2002. TBX-3, the gene mutated in Ulnar-Mammary Syndrome, is a negative regulator of p19ARF and inhibits senescence. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 6567-6572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
