Activated oncogenes promote and cooperate with chromosomal instability for neoplastic transformation
- PMID: 15175263
- PMCID: PMC420357
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1165204
Activated oncogenes promote and cooperate with chromosomal instability for neoplastic transformation
Abstract
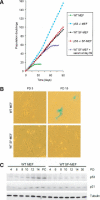
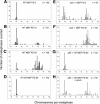
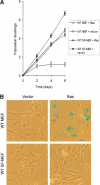
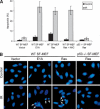
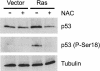
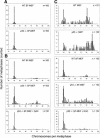
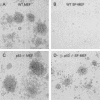
Most cancer cells are aneuploid. The chromosomal instability hypothesis contends that aneuploidy is the catalyst for transformation, whereas the gene mutation hypothesis asserts that cancer is driven by mutations to proto-oncogenes and tumor-suppressor genes, with the aneuploidy a side effect of tumorigenesis. Because genotoxic stress induced by "culture shock" can obscure the transforming potential of exogenous genes, we cultured wild-type and p53(-/-) mouse embryo fibroblasts in a more physiological (serum-free) environment. Under these conditions, the cells were immortal and, more importantly, chromosomally stable. Expression of oncogenic H-RasV12 did not induce senescence, but sensitized these cells to p53-dependent apoptosis. In addition, H-RasV12 induced chromosomal instability, as well as accumulation and phosphorylation of p53. Significantly, whereas cells grown under standard conditions could be transformed by coexpression of H-RasV12 and E1A, the chromosomally stable cells were refractory to transformation, as measured by anchorage-independent growth and tumor formation in nude mice. These oncogenes required a third genetic alteration that abolished the p53 pathway to create a permissive environment that promotes rapid chromosomal instability and transformation. Oncogene-induced chromosomal instability and transformation was attenuated by antioxidants. These data indicate that chromosomal instability could be a catalyst for oncogenic transformation, and bring together aspects of the chromosomal instability hypothesis and the gene mutation hypothesis for tumorigenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Artandi, S.E., Chang, S., Lee, S.L., Alson, S., Gottlieb, G.J., Chin, L., and DePinho, R.A. 2000. Telomere dysfunction promotes non-reciprocal translocations and epithelial cancers in mice. Nature 406: 641-645. - PubMed
-
- Aruoma, O.I., Halliwell, B., Hoey, B.M., and Butler, J. 1989. The antioxidant action of N-acetylcysteine: Its reaction with hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, superoxide, and hypochlorous acid. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 6: 593-597. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, D. and Sato, G. 1980. Methods for growth of cultured cells in serum-free medium. Anal. Biochem. 102: 255-270. - PubMed
-
- Blasco, M.A., Lee, H.W., Hande, M.P., Samper, E., Lansdorp, P.M., DePinho, R.A., and Greider, C.W. 1997. Telomere shortening and tumor formation by mouse cells lacking telomerase RNA. Cell 91: 25-34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
