Quorum sensing regulates type III secretion in Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- PMID: 15175293
- PMCID: PMC419960
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.12.3794-3805.2004
Quorum sensing regulates type III secretion in Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Abstract
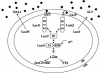
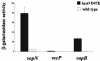
In a process known as quorum sensing, bacteria communicate with one another by producing, releasing, detecting, and responding to signal molecules called autoinducers. Vibrio harveyi, a marine pathogen, uses two parallel quorum-sensing circuits, each consisting of an autoinducer-sensor pair, to control the expression of genes required for bioluminescence and a number of other target genes. Genetic screens designed to discover autoinducer-regulated targets in V. harveyi have revealed genes encoding components of a putative type III secretion (TTS) system. Using transcriptional reporter fusions and TTS protein localization studies, we show that the TTS system is indeed functional in V. harveyi and that expression of the genes encoding the secretion machinery requires an intact quorum-sensing signal transduction cascade. The newly completed genome of the closely related marine bacterium Vibrio parahaemolyticus, which is a human pathogen, shows that it possesses the genes encoding both of the V. harveyi-like quorum-sensing signaling circuits and that it also has a TTS system similar to that of V. harveyi. We show that quorum sensing regulates TTS in V. parahaemolyticus. Previous reports connecting quorum sensing to TTS in enterohemorrhagic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli show that quorum sensing activates TTS at high cell density. Surprisingly, we find that at high cell density (in the presence of autoinducers), quorum sensing represses TTS in V. harveyi and V. parahaemolyticus.
Figures





Comment in
-
Reciprocal regulation of bioluminescence and type III protein secretion in Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in response to diffusible chemical signals.J Bacteriol. 2004 Jun;186(12):3674-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.12.3674-3676.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15175279 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Three parallel quorum-sensing systems regulate gene expression in Vibrio harveyi.J Bacteriol. 2004 Oct;186(20):6902-14. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.20.6902-6914.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15466044 Free PMC article.
-
The Vibrio harveyi quorum-sensing system uses shared regulatory components to discriminate between multiple autoinducers.Genes Dev. 2006 Oct 1;20(19):2754-67. doi: 10.1101/gad.1466506. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 17015436 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal regulation of bioluminescence and type III protein secretion in Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in response to diffusible chemical signals.J Bacteriol. 2004 Jun;186(12):3674-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.12.3674-3676.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15175279 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Quorum Sensing Gene Regulation by LuxR/HapR Master Regulators in Vibrios.J Bacteriol. 2017 Sep 5;199(19):e00105-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00105-17. Print 2017 Oct 1. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28484045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxazaborolidine derivatives inducing autoinducer-2 signal transduction in Vibrio harveyi.Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Feb 15;16(4):1596-604. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.11.032. Epub 2007 Nov 17. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18053731 Review.
Cited by
-
Fitness factors in vibrios: a mini-review.Microb Ecol. 2013 May;65(4):826-51. doi: 10.1007/s00248-012-0168-x. Epub 2013 Jan 10. Microb Ecol. 2013. PMID: 23306394 Review.
-
Monitoring of Vibrio harveyi quorum sensing activity in real time during infection of brine shrimp larvae.ISME J. 2012 Dec;6(12):2314-9. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2012.58. Epub 2012 Jun 7. ISME J. 2012. PMID: 22673627 Free PMC article.
-
The quorum-sensing hybrid histidine kinase LuxN of Vibrio harveyi contains a periplasmically located N terminus.J Bacteriol. 2007 Apr;189(7):2945-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.01723-06. Epub 2007 Jan 26. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17259316 Free PMC article.
-
Three parallel quorum-sensing systems regulate gene expression in Vibrio harveyi.J Bacteriol. 2004 Oct;186(20):6902-14. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.20.6902-6914.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15466044 Free PMC article.
-
A small-RNA-mediated negative feedback loop controls quorum-sensing dynamics in Vibrio harveyi.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Nov;70(4):896-907. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06452.x. Epub 2008 Sep 18. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18808382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bassler, B. L., M. Wright, R. E. Showalter, and M. R. Silverman. 1993. Intercellular signalling in Vibrio harveyi: sequence and function of genes regulating expression of luminescence. Mol. Microbiol. 9:773-786. - PubMed
-
- Bassler, B. L., M. Wright, and M. R. Silverman. 1994. Multiple signalling systems controlling expression of luminescence in Vibrio harveyi: sequence and function of genes encoding a second sensory pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 13:273-286. - PubMed
-
- Bassler, B. L., M. Wright, and M. R. Silverman. 1994. Sequence and function of LuxO, a negative regulator of luminescence in Vibrio harveyi. Mol. Microbiol. 12:403-412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

