Genetic characterization of a multicomponent signal transduction system controlling the expression of cable pili in Burkholderia cenocepacia
- PMID: 15175296
- PMCID: PMC419935
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.12.3826-3836.2004
Genetic characterization of a multicomponent signal transduction system controlling the expression of cable pili in Burkholderia cenocepacia
Abstract
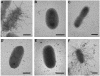
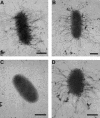
Cable pili are peritrichous organelles expressed by certain strains of Burkholderia cenocepacia, believed to facilitate colonization of the lower respiratory tract in cystic fibrosis patients. The B. cenocepacia cblBACDS operon encodes the structural and accessory proteins required for the assembly of cable pili, as well as a gene designated cblS, predicted to encode a hybrid sensor kinase protein of bacterial two-component signal transduction systems. In this study we report the identification of two additional genes, designated cblT and cblR, predicted to encode a second hybrid sensor kinase and a response regulator, respectively. Analyses of the deduced amino acid sequences of the cblS and cblT gene products revealed that both putative sensor kinases have transmitter and receiver domains and that the cblT gene product has an additional C-terminal HPt domain. Mutagenesis of the cblS, cblT, or cblR gene led to a block in expression of CblA, the major pilin subunit, and a severe decrease in cblA transcript abundance. Using transcriptional fusion analyses, the decrease in the abundance of the cblA transcript in the cblS, cblT, and cblR mutants was shown to be due to a block in transcription from the cblB-proximal promoter, located upstream of the cblBACDS operon. Furthermore, ectopic expression of either cblS or cblR in wild-type B. cenocepacia strain BC7 led to a significant increase, while ectopic expression of cblT resulted in a dramatic decrease, in abundance of the CblA major pilin and the cblA transcript. Our results demonstrate that the B. cenocepacia cblS, cblT, and cblR genes are essential for cable pilus expression and that their effect is exerted at the level of transcription of the cblBACDS operon. These findings are consistent with the proposed function of the cblSTR gene products as a multicomponent signal transduction pathway controlling the expression of cable pilus biosynthetic genes in B. cenocepacia.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of cable pilus gene expression in Burkholderia cenocepacia.J Bacteriol. 2004 Feb;186(4):1009-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.4.1009-1020.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 14761995 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and molecular analysis of cable pilus biosynthesis genes in Burkholderia cepacia.Microbiology (Reading). 2003 Apr;149(Pt 4):961-971. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26176-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2003. PMID: 12686638
-
Adherence and autoaggregation phenotypes of a Burkholderia cenocepacia cable pilus mutant.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2003 Nov 21;228(2):287-97. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00785-7. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2003. PMID: 14638436
-
Burkholderia cenocepacia in cystic fibrosis: epidemiology and molecular mechanisms of virulence.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010 Jul;16(7):821-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03237.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010. PMID: 20880411 Review.
-
Prokaryotic signal transduction mediated by sensor and regulator protein pairs.Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:311-36. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001523. Annu Rev Genet. 1989. PMID: 2694934 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Identification of potential therapeutic targets for Burkholderia cenocepacia by comparative transcriptomics.PLoS One. 2010 Jan 15;5(1):e8724. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008724. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20090946 Free PMC article.
-
Intraspecies signaling involving the diffusible signal factor BDSF (cis-2-dodecenoic acid) influences virulence in Burkholderia cenocepacia.J Bacteriol. 2009 Aug;191(15):5013-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00473-09. Epub 2009 May 29. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19482924 Free PMC article.
-
The Hybrid Histidine Kinase LadS Forms a Multicomponent Signal Transduction System with the GacS/GacA Two-Component System in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.PLoS Genet. 2016 May 13;12(5):e1006032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006032. eCollection 2016 May. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27176226 Free PMC article.
-
Cable pili and the 22-kilodalton adhesin are required for Burkholderia cenocepacia binding to and transmigration across the squamous epithelium.Infect Immun. 2005 Sep;73(9):5426-37. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.9.5426-5437.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16113259 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Kinases of ESKAPE Pathogens for Therapeutic Interventions.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2024;22(3):276-297. doi: 10.2174/0118715257267497231128093529. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39403051 Review.
References
-
- Boyd, J. M., T. Koga, and S. Lory. 1994. Identification and characterization of PilS, an essential regulator of pilin expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Gen. Genet. 3:565-574. - PubMed
-
- Burbulys, D., K. A. Trach, and J. A. Hoch. 1991. Initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell 64:545-552. - PubMed
-
- Burkholder, W. H. 1950. Sour skin: a bacterial rot of onion bulbs. Phytopathology 40:115-117.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

