Dopamine-glutamate interactions controlling prefrontal cortical pyramidal cell excitability involve multiple signaling mechanisms
- PMID: 15175382
- PMCID: PMC6729185
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1021-04.2004
Dopamine-glutamate interactions controlling prefrontal cortical pyramidal cell excitability involve multiple signaling mechanisms
Abstract
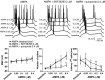
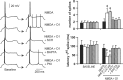
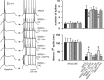
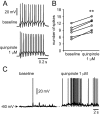
Although the importance of dopamine (DA) for prefrontal cortical (PFC) cognitive functions is widely recognized, the nature of DA actions in the PFC remains controversial. A critical component in DA actions is its modulation of glutamate transmission, which can be different when specific receptors are activated. To obtain a clear picture of cellular mechanisms involved in these interactions, we studied the effects of DA-glutamate coactivation on pyramidal cell excitability in brain slices obtained from developmentally mature rats using whole-cell patch-clamp recordings. Bath application of NMDA, AMPA, and the D1 agonist SKF38393 induced concentration-dependent excitability increases, whereas bath application of the D2 receptor agonist quinpirole induced a concentration-dependent excitability decrease. The NMDA-mediated response was potentiated by SKF38393. This NMDA-D1 synergism required postsynaptic intracellular Ca2+ and protein kinase A (PKA) and was independent of membrane depolarization. On the other hand, the excitatory effects of both NMDA and AMPA were attenuated by a D2 agonist. Surprisingly, the D2-NMDA interaction was also blocked by the GABA(A) antagonists bicuculline and picrotoxin, suggesting that the inhibitory action of D2 receptors on NMDA-induced responses in the PFC may be mediated by GABAergic interneurons. In contrast, the D2-AMPA interaction involves inhibition of PKA and activation of phospholipase lipase C-IP3 and intracellular Ca2+ at a postsynaptic level. Thus, the modulatory actions of D1 and D2 receptors on PFC pyramidal cell excitability are mediated by multiple intracellular mechanisms and by activation of GABA(A) receptors, depending on the glutamate receptor subtypes involved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of NMDA receptors by dopamine D4 signaling in prefrontal cortex.J Neurosci. 2003 Oct 29;23(30):9852-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-30-09852.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14586014 Free PMC article.
-
Post-pubertal disruption of medial prefrontal cortical dopamine-glutamate interactions in a developmental animal model of schizophrenia.Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Oct 1;62(7):730-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.10.012. Epub 2007 Jan 3. Biol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17207473 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D1 and D4 receptor subtypes differentially modulate recurrent excitatory synapses in prefrontal cortical pyramidal neurons.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Feb;31(2):318-38. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300829. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006. PMID: 16052247
-
Dopamine/glutamate interaction as studied by combining turning behaviour and c-Fos expression.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1997 Jul;21(4):505-9. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(96)00031-0. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1997. PMID: 9195609 Review.
-
Dopamine's Actions in Primate Prefrontal Cortex: Challenges for Treating Cognitive Disorders.Pharmacol Rev. 2015 Jul;67(3):681-96. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.010512. Pharmacol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26106146 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sleep and plasticity in schizophrenia.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2015;25:433-58. doi: 10.1007/7854_2014_366. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25608723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
D1 receptors in the anterior cingulate cortex modulate basal mechanical sensitivity threshold and glutamatergic synaptic transmission.Mol Brain. 2020 Sep 5;13(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s13041-020-00661-x. Mol Brain. 2020. PMID: 32891169 Free PMC article.
-
Interhemispheric regulation of the rat medial prefrontal cortical glutamate stress response: role of local GABA- and dopamine-sensitive mechanisms.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Feb;234(3):353-363. doi: 10.1007/s00213-016-4468-6. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 27822602
-
Repeated amphetamine administration decreases D1 dopamine receptor-mediated inhibition of voltage-gated sodium currents in the prefrontal cortex.J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 22;26(12):3164-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2375-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16554467 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine modulation of learning and memory in the prefrontal cortex: insights from studies in primates, rodents, and birds.Front Neural Circuits. 2014 Aug 5;8:93. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2014.00093. eCollection 2014. Front Neural Circuits. 2014. PMID: 25140130 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cepeda C, Levine MS (1998) Dopamine and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor interactions in the neostriatum. Dev Neurosci 20: 1–18. - PubMed
-
- Cepeda C, Radisavljevic Z, Peacock W, Levine MS, Buchwald NA (1992) Differential modulation by dopamine of responses evoked by excitatory amino acids in human cortex. Synapse 11: 330–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
