Dopamine modulates use-dependent plasticity of inhibitory synapses
- PMID: 15175385
- PMCID: PMC6729188
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4979-03.2004
Dopamine modulates use-dependent plasticity of inhibitory synapses
Abstract
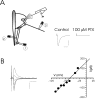
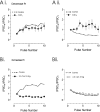
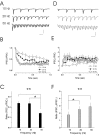
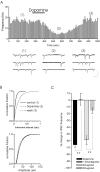
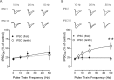
The release of the hormones oxytocin (OT) and vasopressin (VP) into the circulation is dictated by the electrical activity of hypothalamic magnocellular neurosecretory cells (MNCs). In the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN), MNC neuronal activity is exquisitely sensitive to changes in input from inhibitory GABAergic synapses. To explore the hypothesis that efficacy at these synapses is dictated by the rate at which a given synapse is activated, we obtained whole-cell recordings from MNCs in postnatal day 21-27 male Sprague Dawley rat brain slices. IPSCs were elicited by electrically stimulating GABAergic projections from either the suprachiasmatic nucleus or putative interneuron populations immediately ventral to the fornix at 5, 10, 20, and 50 Hz. Short-term plasticity was observed at 88% of the synapses tested. Of this group, synaptic depression was observed in 58%, and synaptic facilitation was observed in 41%. Identification of cells using a combined electrophysiological and immunohistochemical approach revealed a strong correlation between cell phenotype and the nature of the plasticity. Short-term facilitation was observed preferentially in OT cells (86%), whereas short-term depression was predominant in VP neurons (69%). We next examined the effects of dopamine, which increases MNC excitability, on short-term plasticity. Activation of presynaptic D(4) receptors decreased the frequency of miniature IPSCs and prevented the development of synaptic depression at higher rates of activity. Synaptic facilitation, however, was unaffected by dopamine. These findings demonstrate that, by lowering GABA release probability, dopamine confers high-pass filtering properties to the majority of inhibitory synapses onto MNCs in PVN.
Figures




References
-
- Azdad K, Piet R, Poulain DA, Oliet SH (2003) Dopamine D4 receptor-mediated presynaptic inhibition of GABAergic transmission in the rat supraoptic nucleus. J Neurophysiol 90: 559–565. - PubMed
-
- Bertram R, Arnot MI, Zamponi GW (2002) Role for G protein Gbeta-gamma isoform specificity in synaptic signal processing: a computational study. J Neurophysiol 87: 2612–2623. - PubMed
-
- Bertram R, Swanson J, Yousef M, Feng ZP, Zamponi GW (2003) A minimal model for G protein-mediated synaptic facilitation and depression. J Neurophysiol 90: 1643–1653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
