Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein regulates proliferation and growth inhibition by nitric oxide in vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 15178555
- PMCID: PMC1382167
- DOI: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000134705.39654.53
Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein regulates proliferation and growth inhibition by nitric oxide in vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
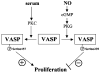
Objective: Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) was identified as a substrate for cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). It is preferentially phosphorylated at serine239 by PKG, whereas serine157 is a preferred phosphorylation site for PKA. In addition, serine157 is phosphorylated by PKC in response to serum. We have investigated the effects of VASP and VASP phosphorylation at serine157 and serine239 on smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation and nitric oxide (NO)-mediated growth inhibition.
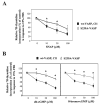
Methods and results: Aortic SMCs derived from VASP-deficient mice were transduced with retroviral vectors encoding either wild-type VASP or VASP mutants (S157A-VASP and S239A-VASP), in which serine157 and serine239, respectively, were replaced by a nonphosphorylatable amino acid, alanine. Expression of wt-VASP and S239A-VASP significantly increased proliferation, whereas expression of S157A-VASP was inhibitory. Expression of S239A-VASP rendered SMCs less sensitive to growth inhibition by the NO donor, S-nitroso-n-acetylpenicillamine, when compared with cells expressing wt-VASP. Similar effects were observed in cultured rat SMCs in which wt-VASP, S157A-VASP, and S239A-VASP were expressed.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that VASP phosphorylation at serine157 is required for the growth-stimulatory effect of VASP in SMCs, whereas VASP phosphorylation at serine239 is involved in the growth inhibitory effects of NO on SMCs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
VASP phosphorylation at serine239 regulates the effects of NO on smooth muscle cell invasion and contraction of collagen.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Jan;222(1):230-7. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21942. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19798690 Free PMC article.
-
Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein is a substrate for protein kinase C.FEBS Lett. 2004 Jan 2;556(1-3):211-5. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)01435-2. FEBS Lett. 2004. PMID: 14706852
-
Resistance to the nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine 5'-monophosphate/protein kinase G pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells from the obese Zucker rat, a classical animal model of insulin resistance: role of oxidative stress.Endocrinology. 2008 Apr;149(4):1480-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0920. Epub 2007 Dec 13. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18079207
-
The role of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein in podocyte functioning.Cell Biol Int. 2019 Oct;43(10):1092-1101. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11149. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Cell Biol Int. 2019. PMID: 30968998 Review.
-
Novel protein kinase targets in vascular smooth muscle therapeutics.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2017 Apr;33:12-16. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28388507 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of shRNA-mediated silencing of PDE5A3 on intracellular cGMP and free Ca2+ levels and human prostate smooth muscle cell proliferation from benign prostatic hyperplasia.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Apr;21(4):322. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9753. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33732295 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylated vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein is localized on mitotic spindles of the gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Dec 14;12(46):7478-81. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7478. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17167837 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoskeleton assembly at endothelial cell-cell contacts is regulated by alphaII-spectrin-VASP complexes.J Cell Biol. 2008 Jan 14;180(1):205-19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200709181. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18195108 Free PMC article.
-
Cone photoreceptor phosphodiesterase PDE6H inhibition regulates cancer cell growth and metabolism, replicating the dark retina response.Cancer Metab. 2024 Feb 13;12(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40170-023-00326-y. Cancer Metab. 2024. PMID: 38350962 Free PMC article.
-
Differential VASP phosphorylation controls remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton.J Cell Sci. 2009 Nov 1;122(Pt 21):3954-65. doi: 10.1242/jcs.044537. Epub 2009 Oct 13. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19825941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reinhard M, Jarchau T, Walter U. Actin-based motility: stop and go with Ena/VASP proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:243–249. - PubMed
-
- Krause M, Bear JE, Loureiro JJ, Gertler FB. The Ena/VASP enigma. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:4721–4726. - PubMed
-
- Kwiatkowski AV, Gertler FB, Loureiro JJ. Function and regulation of Ena/VASP proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2003;13:386–392. - PubMed
-
- Butt E, Abel K, Krieger M, Palm D, Hoppe V, Walter U. cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation sites of the focal adhesion vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) in Vitro and in intact human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:14509–14517. - PubMed
-
- Smolenski A, Poller W, Walter U, Lohmann SM. Regulation of human endothelial cell focal adhesion sites and migration by cGMP-dependent protein kinase I. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:25723–25732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

