LNP 906, the first high-affinity photoaffinity ligand selective for I1 imidazoline receptors
- PMID: 15178642
- PMCID: PMC1574957
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705784
LNP 906, the first high-affinity photoaffinity ligand selective for I1 imidazoline receptors
Erratum in
- Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Aug;142(8):1368. Dragan, Urosevic [corrected to Urosevic, Dragan]; Stephan, Schann [corrected to Schann, Stephan]; Jean-Daniel, Ehrhardt [corrected to Ehrhardt, Jean-Daniel]; Pascal, Bousquet [corrected to Bousquet, Pascal]; Hugues, Greney [corrected to Greney, Hugues]
Abstract
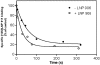
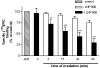
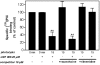
1 The hypotensive effect of imidazoline-like drugs, such as clonidine, was attributed both to alpha2-adrenergic receptors and nonadrenergic imidazoline receptors, which are divided into I1, I2 and I3 subtypes. 2 We have recently synthesized a derivative of (2-(2-chloro-4-iodo-phenylamino)-5-methyl-pyrroline (LNP 911), the first high-affinity and selective ligand for I1 receptors (I1R), with a photoactivable function (LNP 906). 3 This work aims to test whether this derivative retained the binding properties of LNP 911 and bound irreversibly to I1R. 4 Binding studies showed that LNP 906 exhibited nanomolar affinity for I1R and was selective for I1R over I2 receptors and alpha2-adrenergic receptors (alpha2Ars). 5 Upon exposure to u.v. light, LNP 906 irreversibly blocked the binding of [125I]-paraiodoclonidine (PIC) to I1R, time- and dose-dependently, on PC12 cell membranes and interacted with I1R in a reversible and competitive manner in the absence of light. Pharmacological studies showed that this blockade was prevented by the concomitant presence of rilmenidine (a well-known I1 agonist), but not by rauwolscine (an alpha2 antagonist). 6 Finally, LNP 906 clearly antagonized the decrease in forskolin-stimulated cAMP level induced by rilmenidine, but not by melatonin. 7 These results indicate that LNP 906 is the first high-affinity and selective photoaffinity ligand for I1R and that it behaves as an I1R antagonist.
Figures

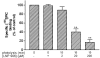

Similar articles
-
[125I]2-(2-chloro-4-iodo-phenylamino)-5-methyl-pyrroline (LNP 911), a high-affinity radioligand selective for I1 imidazoline receptors.Mol Pharmacol. 2002 Jul;62(1):181-91. doi: 10.1124/mol.62.1.181. Mol Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12065769
-
Comparison of ligand binding affinities at human I1-imidazoline binding sites and the high affinity state of alpha-2 adrenoceptor subtypes.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996 Nov;279(2):694-702. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996. PMID: 8930173
-
Nonadrenergic imidazoline binding sites on human platelets.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Dec;267(3):1493-502. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993. PMID: 8263811
-
The renaissance of centrally acting antihypertensive drugs.J Hypertens Suppl. 1999 Aug;17(3):S15-21. J Hypertens Suppl. 1999. PMID: 10489094 Review.
-
Imidazoline receptors and their endogenous ligands.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1996;36:511-44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.36.040196.002455. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1996. PMID: 8725400 Review.
References
-
- BOUSQUET P., BRUBAN V., SCHANN S., FELDMAN J. Imidazoline receptors: a challenge. Pharm. Acta Helv. 2000;74:205–209. - PubMed
-
- BOUSQUET P., FELDMAN J. Drugs acting on imidazoline receptors: a review of their pharmacology, their use in blood pressure control and their potential interest in cardioprotection. Drugs. 1999;58:799–812. - PubMed
-
- BOUSQUET P., FELDMAN J., SCHWARTZ J. Central cardiovascular effects of alpha-adrenergic drugs: differences between catecholamines and imidazolines. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1984;230:232–236. - PubMed
-
- BRADFORD M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the existence of quantitation of protein utilizing the principle protein–dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976;72:248–252. - PubMed
-
- BRICCA G., GRENEY H., ZHANG J., DONTENWILL M., STUTZMANN J., BELCOURT D., BOUSQUET P. Human brain imidazoline receptors: further characterization with [3H] clonidine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994;266:25–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

