How do site-specific DNA-binding proteins find their targets?
- PMID: 15178741
- PMCID: PMC434431
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh624
How do site-specific DNA-binding proteins find their targets?
Abstract
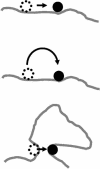
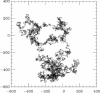
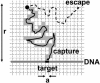
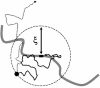
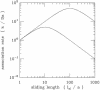
Essentially all the biological functions of DNA depend on site-specific DNA-binding proteins finding their targets, and therefore 'searching' through megabases of non-target DNA. In this article, we review current understanding of how this sequence searching is done. We review how simple diffusion through solution may be unable to account for the rapid rates of association observed in experiments on some model systems, primarily the Lac repressor. We then present a simplified version of the 'facilitated diffusion' model of Berg, Winter and von Hippel, showing how non-specific DNA-protein interactions may account for accelerated targeting, by permitting the protein to sample many binding sites per DNA encounter. We discuss the 1-dimensional 'sliding' motion of protein along non-specific DNA, often proposed to be the mechanism of this multiple site sampling, and we discuss the role of short-range diffusive 'hopping' motions. We then derive the optimal range of sliding for a few physical situations, including simple models of chromosomes in vivo, showing that a sliding range of approximately 100 bp before dissociation optimizes targeting in vivo. Going beyond first-order binding kinetics, we discuss how processivity, the interaction of a protein with two or more targets on the same DNA, can reveal the extent of sliding and we review recent experiments studying processivity using the restriction enzyme EcoRV. Finally, we discuss how single molecule techniques might be used to study the dynamics of DNA site-specific targeting of proteins.
Figures


References
-
- Ptashne M. and Gann,A. (2001) Genes and Signals. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
-
- Riggs A.D., Bourgeois,S. and Cohn,M. (1970) The lac repressor-operator interaction. III. Kinetic studies. J. Mol. Biol., 53, 401–417. - PubMed
-
- Berg O.G. and von Hippel,P.H. (1985) Diffusion-controlled macromolecular interactions. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem., 14, 131–160. - PubMed
-
- von Hippel P.H. and Berg,O.G. (1989) Facilitated target location in biological systems. J. Biol. Chem., 264, 675–678. - PubMed
-
- Shimamoto N. (1999) One-dimensional diffusion of proteins along DNA. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 15293–15296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

