Visualization of ribosome-recycling factor on the Escherichia coli 70S ribosome: functional implications
- PMID: 15178758
- PMCID: PMC428444
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0401904101
Visualization of ribosome-recycling factor on the Escherichia coli 70S ribosome: functional implications
Abstract
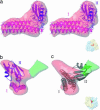
After the termination step of protein synthesis, a deacylated tRNA and mRNA remain associated with the ribosome. The ribosome-recycling factor (RRF), together with elongation factor G (EF-G), disassembles this posttermination complex into mRNA, tRNA, and the ribosome. We have obtained a three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopic map of a complex of the Escherichia coli 70S ribosome and RRF. We find that RRF interacts mainly with the segments of the large ribosomal subunit's (50S) rRNA helices that are involved in the formation of two central intersubunit bridges, B2a and B3. The binding of RRF induces considerable conformational changes in some of the functional domains of the ribosome. As compared to its binding position derived previously by hydroxyl radical probing study, we find that RRF binds further inside the intersubunit space of the ribosome such that the tip of its domain I is shifted (by approximately 13 A) toward protein L5 within the central protuberance of the 50S subunit, and domain II is oriented more toward the small ribosomal subunit (30S). Overlapping binding sites of RRF, EF-G, and the P-site tRNA suggest that the binding of EF-G would trigger the removal of deacylated tRNA from the P site by moving RRF toward the ribosomal E site, and subsequent removal of mRNA may be induced by a shift in the position of 16S rRNA helix 44, which harbors part of the mRNA.
Figures




References
-
- Carter, A. P., Clemons, W. M., Jr., Brodersen, D. E., Morgan-Warren, R. J., Hartsch, T., Wimberly, B. T. & Ramakrishnan, V. (2001) Science 291, 498–501. - PubMed
-
- Stark, H., Rodnina, M. V., Rinke-Appel, J., Brimacombe, R., Wintermeyer, W. & van Heel, M. (1997) Nature 389, 403–406. - PubMed
-
- Klaholz, B. P., Pape, T., Zavialov, A. V., Myasnikov, A. G., Orlova, E. V., Vestergaard, B., Ehrenberg, M. & van Heel, M. (2003) Nature 421, 90–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

