PKA-phosphorylation of PDE4D3 facilitates recruitment of the mAKAP signalling complex
- PMID: 15182229
- PMCID: PMC1133866
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20040846
PKA-phosphorylation of PDE4D3 facilitates recruitment of the mAKAP signalling complex
Abstract
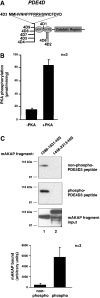
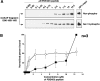
mAKAP (muscle-selective A-kinase-anchoring protein) co-ordinates a cAMP-sensitive negative-feedback loop comprising PKA (cAMP-dependent protein kinase) and the cAMP-selective PDE4D3 (phosphodiesterase 4D3). In vitro and cellular experiments demonstrate that PKA-phosphorylation of PDE4D3 on Ser-13 increases the affinity of PDE4D3 for mAKAP. Our data suggest that activation of mAKAP-anchored PKA enhances the recruitment of PDE4D3, allowing for quicker signal termination.
Figures



References
-
- Colledge M., Scott J. D. AKAPs: from structure to function. Trends Cell Biol. 1999;9:216–221. - PubMed
-
- Tasken K., Aandahl E. M. Localized effects of cAMP mediated by distinct routes of protein kinase A. Physiol. Rev. 2004;84:137–167. - PubMed
-
- Francis S. H., Turko I. V., Corbin J. D. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: relating structure and function. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2001;65:1–52. - PubMed
-
- Yarwood S. J., Steele M. R., Scotland G., Houslay M. D., Bolger G. B. The RACK1 signaling scaffold protein selectively interacts with the cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE4D5 isoform. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:14909–14917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

