Nanogold-plasmon-resonance-based glucose sensing
- PMID: 15183773
- PMCID: PMC6986337
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2004.03.032
Nanogold-plasmon-resonance-based glucose sensing
Abstract
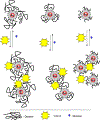
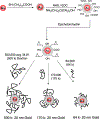
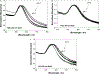
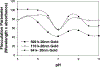
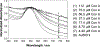
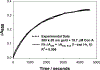
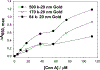
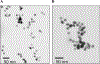
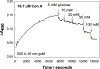
Noble metal nanoparticles are well known for their strong interactions with light through the resonant excitations of the collective oscillations of the conduction electrons on the particles, the so-called surface plasmon resonances. The close proximity of two nanoparticles is known to result in a red-shifted resonance wavelength peak, due to near-field coupling. We have subsequently employed this phenomenon and developed a new approach to glucose sensing, which is based on the aggregation and disassociation of 20-nm gold particles and the changes in plasmon absorption induced by the presence of glucose. High-molecular-weight dextran-coated nanoparticles are aggregated with concanavalin A (Con A), which results in a significant shift and broadening of the gold plasmon absorption. The addition of glucose competitively binds to Con A, reducing gold nanoparticle aggregation and therefore the plasmon absorption when monitored at a near-red arbitrary wavelength. We have optimized our plasmonic-type glucose nanosensors with regard to particle stability, pH effects, the dynamic range for glucose sensing, and the observation wavelength to be compatible with clinical glucose requirements and measurements. In addition, by modifying the amount of dextran or Con A used in nanoparticle fabrication, we can to some extent tune the glucose response range, which means that a single sensing platform could potentially be used to monitor microM --> mM glucose levels in many physiological fluids, such as tears, blood, and urine, where the glucose concentrations are significantly different.
Figures

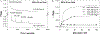
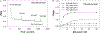
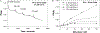
References
-
- Storhoff JJ, Elghanian R, Mucic RC, Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL, One- pot colorimetric differentiation of polynucleotides with single base imperfections using gold nanoparticle probes, J. Am. Chem. Soc 120 (1998) 1959–1964.
-
- Reynolds RA, Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL, Homogeneous, nanoparticle- based quantitative colorimetric detection of oligonucleotides, J. Am. Chem. Soc 122 (2000) 3795–3796.
-
- Elghanian R, Storhoff JJ, Mucic RC, Letsinger RL, Mirkin CA, Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance- dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles, Science 277 (1997) 1078–1081. - PubMed
-
- Sastry M, Lala N, Patil V, Chavan SP, Chittiboyina AG, Optical absorption study of the biotin- avidin interaction on colloidal silver and gold particles, Langmuir 14 (1998) 4138–4142.
-
- Cobbe S, Connolly S, Ryan D, Nagle L, Eritja R, Fitzmaurice DJ, DNA- controlled assembly of protein-modified gold nanocrystals, J. Phys. Chem. B 107 (2003) 470–477.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

