Biology of the metabolically diverse genus Gordonia
- PMID: 15184112
- PMCID: PMC427784
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.6.3195-3204.2004
Biology of the metabolically diverse genus Gordonia
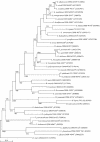
Figures

References
-
- Abbad-Andaloussi, S., M. Warzywoda, and F. Monot. 2003. Microbial desulfurization of diesel oils by selected bacterial strains. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 58:505-513.
-
- Arenskötter, M., D. Baumeister, M. M. Berekaa, G. Pötter, R. M. Kroppenstedt, A. Linos, and A. Steinbüchel. 2001. Taxonomic characterization of two rubber degrading bacteria belonging to the species Gordonia polyisoprenivorans and analysis of hypervariable regions of 16S rDNA sequences. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 205:277-282. - PubMed
-
- Aspinall, G. O., D. Chatterjee, and P. J. Brennan. 1995. The variable surface of mycobacteria: structures, synthesis of epitopes, and biological properties. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 51:169-242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

