Evolutionary relationships of primary prokaryotic endosymbionts of whiteflies and their hosts
- PMID: 15184137
- PMCID: PMC427722
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.6.3401-3406.2004
Evolutionary relationships of primary prokaryotic endosymbionts of whiteflies and their hosts
Abstract
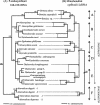
Whiteflies (Hemiptera: Sternorrhyncha: Aleyrodidae) are plant sap-sucking insects that harbor prokaryotic primary endosymbionts (P-endosymbionts) within specialized cells located in their body cavity. Four-kilobase DNA fragments containing 16S-23S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) were amplified from the P-endosymbiont of 24 whiteflies from 22 different species of 2 whitefly subfamilies. In addition, 3-kb DNA fragments containing mitochondrial cytB, nd1, and large-subunit rDNA (LrDNA) were amplified from 17 whitefly species. Comparisons of the P-endosymbiont (16S-23S rDNA) and host (cytB-nd1-LrDNA) phylogenetic trees indicated overall congruence consistent with a single infection of a whitefly ancestor with a bacterium and subsequent cospeciation (cocladogenesis) of the host and the P-endosymbiont. On the basis of both the P-endosymbiont and host trees, the whiteflies could be subdivided into at least five clusters. The major subdivision was between the subfamilies Aleyrodinae and Aleurodicinae. Unlike the P-endosymbionts of may other insects, the P-endosymbionts of whiteflies were related to Pseudomonas and possibly to the P-endosymbionts of psyllids. The lineage consisting of the P-endosymbionts of whiteflies is given the designation "Candidatus Portiera" gen. nov., with a single species, "Candidatus Portiera aleyrodidarum" sp. nov.
Figures

References
-
- Aksoy, S., X. Chen, and V. Hypsa. 1997. Phylogeny and potential transmission routes of midgut-associated endosymbionts of tsetse (Diptera: Glossinidae). Insect Mol. Biol. 6:183-190. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, L., M. L. Thao, C. J. Funk, B. W. Falk, J. C. K. Ng, and P. Baumann. 2004. Sequence analysis of DNA fragments from the genome of the primary endosymbiont of Bemisia tabaci. Curr. Microbiol. 48:77-81. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, P., N. A. Moran, and L. Baumann. 2000. Bacteriocyte-associated endosymbionts of insects. In M. Dworkin (ed.), The prokaryotes. [Online.] Springer, New York, N.Y. http://link.springer.de/link/service/books/10125.
-
- Buchner, P. 1965. Endosymbiosis of animals with plant microorganisms, p. 332-338. John Wiley and Sons Interscience, New York, N.Y.
-
- Campbell, B. C., J. D. Steffen-Campbell, and R. J. Gill. 1996. Origin and radiation of whiteflies: an initial molecular phylogenetic assessment, p. 29-51. In D. Gerling and R. T. Mayer (Ed.), Bemisia 1995: taxonomy, biology, damage, control and management. Intercept, Andover, United Kingdom.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

