Rapid quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA by automated sample preparation and real-time PCR
- PMID: 15184417
- PMCID: PMC427868
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.6.2445-2449.2004
Rapid quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA by automated sample preparation and real-time PCR
Abstract
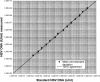
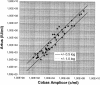
Monitoring of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA in serum by molecular methods has become the standard for assessment of the replicative activity of HBV. Several molecular assays for the detection and quantification of HBV DNA have been described. However, they usually lack automated sample preparation. Moreover, those assays, which are based on PCR, are limited by a short dynamic range (2 to 3 log units). In the present study, the use of RealArt HBV LC PCR Reagents in conjunction with automated extraction on the COBAS AMPLIPREP analyzer was evaluated. Members of an HBV proficiency program panel were tested; linearity, interassay, and intra-assay variations were determined. The performance of the assay in a routine clinical laboratory was evaluated with a total of 117 clinical specimens. When members of the HBV proficiency program panel were tested by the new molecular assay, the results were found to be within +/-0.5 log unit of the results obtained by reference laboratories. Determination of linearity resulted in a quasilinear curve over more than 6 log units. The interassay variation of the RealArt HBV LC PCR Reagents by use of the automated sample preparation protocol ranged from 16 to 73%, and the intra-assay variation ranged from 9 to 40%. When clinical samples were tested by the new assay with the automated sample preparation protocol and the results were compared with those obtained by the COBAS AMPLICOR HBV MONITOR Test with manual sample preparation, the results for 76% of all samples with positive results by both tests were found to be within +/-0.5 log unit and the results for another 18% were found to be within between 0.5 and 1.0 log unit. In conclusion, the real-time PCR assay with automated sample preparation proved to be suitable for the routine molecular laboratory and required less hands-on time.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the COBAS AmpliPrep-total nucleic acid isolation-COBAS TaqMan hepatitis B virus (HBV) quantitative test and comparison to the VERSANT HBV DNA 3.0 assay.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Apr;44(4):1390-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.4.1390-1399.2006. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16597867 Free PMC article.
-
COBAS AmpliPrep-COBAS TaqMan hepatitis B virus (HBV) test: a novel automated real-time PCR assay for quantification of HBV DNA in plasma.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Mar;45(3):828-34. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00914-06. Epub 2007 Jan 17. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17229858 Free PMC article.
-
Fully automated quantitation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA in human plasma by the COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan system.J Clin Virol. 2006 Apr;35(4):373-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2006.01.003. Epub 2006 Feb 7. J Clin Virol. 2006. PMID: 16461000
-
Evaluation of an automated sample preparation protocol for quantitative detection of hepatitis C virus RNA.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Apr;40(4):1447-50. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.4.1447-1450.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11923371 Free PMC article.
-
Automation of laboratory testing for infectious diseases using the polymerase chain reaction-- our past, our present, our future.J Clin Virol. 2001 Jan;20(1-2):1-6. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6532(00)00148-7. J Clin Virol. 2001. PMID: 11163576 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical features of treatment-naive patients with hepatitis B virus infection: A community-based survey from high- and intermediate-hepatitis B endemicity regions in Southeast China.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Apr;96(16):e6660. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006660. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28422873 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA by SYBR green real-time polymerase chain reaction.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007 Jan;26(1):43-50. doi: 10.1007/s10096-006-0223-y. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17216291
-
Comparison of Hybrid Capture 2 Assay with Real-time-PCR for Detection and Quantitation of Hepatitis B Virus DNA.Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2014 Jan-Jun;4(1):31-35. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1093. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 29264316 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time PCR in clinical microbiology: applications for routine laboratory testing.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Jan;19(1):165-256. doi: 10.1128/CMR.19.1.165-256.2006. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16418529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic range and reproducibility of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA detection and quantification by Cobas Taqman HBV, a real-time semiautomated assay.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Aug;43(8):4251-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.8.4251-4254.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16081992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berger, A, W. Preiser, and H. W. Doerr. 2001. The role of viral load determination for the management of human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 20:23-30. - PubMed
-
- Hendricks, D. A., B. J. Stowe, B. S. Hoo, J. Kolberg, B. D. Irvine, P. D. Neuwald, M. S. Urdea, and R. P. Perrillo. 1995. Quantitation of HBV DNA in human serum using a branched DNA (bDNA) signal amplification assay. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 104:537-546. - PubMed
-
- Ho, S. K., W. C. Yam, E. T. Leung, L. P. Wong, J. K. Leung, K. N. Lai, and T. M. Chan. 2003. Rapid quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA by real-time PCR using fluorescent hybridization probes. J. Med. Microbiol. 52:397-402. - PubMed
-
- Jungkind, D. 2001. Automation of laboratory testing for infectious diseases using the polymerase chain reaction—our past, our present, our future. J. Clin. Virol. 20:1-6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

