Simple, rapid latex agglutination test for serotyping of pneumococci (Pneumotest-Latex)
- PMID: 15184429
- PMCID: PMC427861
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.6.2518-2522.2004
Simple, rapid latex agglutination test for serotyping of pneumococci (Pneumotest-Latex)
Abstract
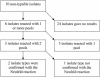
The "gold standard" for epidemiological typing of Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) is the capsular reaction test (Neufeld test) with antisera against the 90 pneumococcal polysaccharide capsules, i.e., serotyping. The method is labor intensive and requires a certain level of experience to be performed satisfactory, and thus it has been restricted for use in specialized reference or research laboratories. Surveillance of the serotype distribution of pneumococci that cause infections is important to secure an optimal composition of pneumococcal vaccines and to monitor antibiotic resistance in pneumococci. At Statens Serum Institut, a simple latex agglutination test for serotyping of pneumococci has been developed. The Pneumotest-Latex kit consists of 14 different pooled pneumococcus antisera (pools A to I and pools P to T) applied to latex particles. In a blind test of 352 isolates (with all 90 serotypes represented), 336 (95.5%) were typed or grouped correctly by the Pneumotest-Latex; in addition, 2 (7%) of 30 strains regarded as nontypeable or rough strains were serotyped, and the serotypes of these two isolates were confirmed by the capsular reaction test with type-specific antisera. The Pneumotest-Latex seems to be a sensitive method for serotyping or grouping of the majority of pneumococcal strains. By use of this ready-to-perform latex agglutination kit (Pneumotest-Latex), serotyping of pneumococci can gain more ground as a tool in prevention of pneumococcal diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct serogrouping of Streptococcus pneumoniae strains in clinical samples by use of a latex agglutination test.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Feb;48(2):593-5. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01651-09. Epub 2009 Dec 9. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20007395 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of broth media on pneumococcal growth and the latex serotyping result.J Microbiol Methods. 2005 May;61(2):181-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2004.11.013. Epub 2004 Dec 28. J Microbiol Methods. 2005. PMID: 15722143
-
Capsular Serotyping of Streptococcus pneumoniae by latex agglutination.J Vis Exp. 2014 Sep 25;(91):51747. doi: 10.3791/51747. J Vis Exp. 2014. PMID: 25285991 Free PMC article.
-
Current methods for capsular typing of Streptococcus pneumoniae.J Microbiol Methods. 2015 Jun;113:41-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Mar 25. J Microbiol Methods. 2015. PMID: 25819558 Review.
-
Impact of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on infections caused by antibiotic-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009 Apr;15 Suppl 3:16-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02726.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009. PMID: 19366365 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel pneumococcal serotypes 6C and 6D: anomaly or harbinger.Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Nov 15;55(10):1379-86. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis691. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Clin Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22903767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular typing of the pneumococcus and its application in epidemiology in sub-Saharan Africa.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013 Mar 14;3:12. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00012. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23503978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pneumococcal Nasopharyngeal Carriage in Young Healthy Children After Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Turkey.Balkan Med J. 2017 Aug 4;34(4):362-366. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.2016.1256. Balkan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28783024 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Serotype Prevalence of Pneumococci Isolated from Middle Ear, Lower Respiratory Tract and Invasive Disease Prior to Vaccination in Iceland.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 26;12(1):e0169210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169210. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28125588 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Approaches and Challenges of Streptococcus pneumoniae Serotyping for Epidemiological Surveillance in the Vaccine Era.Pol J Microbiol. 2023 Jun 14;72(2):103-115. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2023-023. eCollection 2023 Jun 1. Pol J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37314355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arai, S., T. Konda, A. Wada, Y. Matsunaga, N. Okabe, H. Watanabe, and S. Inouye. 2001. Use of antiserum-coated latex particles for serotyping Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microbiol. Immunol. 45:159-162. - PubMed
-
- Chandler, L. J., B. S. Reisner, G. L. Woods, and A. K. Jafri. 2000. Comparison of four methods for identifying Streptococcus pneumoniae. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 37:285-287. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources