Rapid and specific detection of Escherichia coli clonal group A by gene-specific PCR
- PMID: 15184442
- PMCID: PMC427897
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.6.2618-2622.2004
Rapid and specific detection of Escherichia coli clonal group A by gene-specific PCR
Abstract
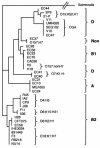
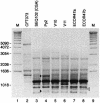
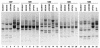
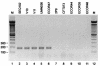
PCR primers specific for the recently described antimicrobial resistance-associated Escherichia coli clonal group A (CGA), a widespread cause of drug-resistant urinary tract infections in the United States, were devised on the basis of a novel single-nucleotide polymorphism identified within the housekeeping gene fumC, i.e., C288T. In comparison with two reference PCR-based fingerprinting methods, ERIC2 PCR and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis, a PCR assay incorporating the new primers provided 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity for the detection of CGA among 138 diverse clinical and reference E. coli isolates. E. coli reference (ECOR) strain 47 was shown to be a member or a close relative of CGA (by ERIC2 PCR and RAPD analysis, respectively) and yielded a positive assay result. The new CGA-specific PCR assay, which exhibited interlaboratory reproducibility and stability under various experimental conditions, should allow the rapid and specific detection of CGA by any laboratory equipped for diagnostic PCR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid and specific detection of the O15:K52:H1 clonal group of Escherichia coli by gene-specific PCR.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Aug;42(8):3841-3. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.8.3841-3843.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15297544 Free PMC article.
-
Clonal groups and the spread of resistance to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Clin Infect Dis. 2005 Apr 15;40(8):1101-7. doi: 10.1086/428727. Epub 2005 Mar 15. Clin Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 15791508
-
Multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli clonal groups causing community-acquired bloodstream infections.J Infect. 2006 Jul;53(1):25-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2005.09.012. Epub 2005 Nov 2. J Infect. 2006. PMID: 16269177
-
Possible animal origin of human-associated, multidrug-resistant, uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Clin Infect Dis. 2005 Jan 15;40(2):251-7. doi: 10.1086/426819. Epub 2004 Dec 22. Clin Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 15655743
-
Occurrence of antibiotic-resistant uropathogenic Escherichia coli clonal group A in wastewater effluents.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Jul;73(13):4180-4. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02225-06. Epub 2007 May 4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17483270 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Temporal trends in antimicrobial resistance and virulence-associated traits within the Escherichia coli sequence type 131 clonal group and its H30 and H30-Rx subclones, 1968 to 2012.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Nov;58(11):6886-95. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03679-14. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 25199783 Free PMC article.
-
Origin of class 1 and 2 integrons and gene cassettes in a population-based sample of uropathogenic Escherichia coli.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Apr;44(4):1347-51. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.4.1347-1351.2006. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16597861 Free PMC article.
-
High levels of multiresistance in quinolone resistant urinary tract isolates of Escherichia coli from Norway; a non clonal phenomen?BMC Res Notes. 2014 Jun 19;7:376. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-376. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 24941949 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial non-susceptibility of cervico-vaginal and rectal Escherichia coli isolates is associated with phylogeny and plasmid carriage.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009 Nov;28(11):1399-403. doi: 10.1007/s10096-009-0788-3. Epub 2009 Jul 29. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19639348
-
The rpoS gene is predominantly inactivated during laboratory storage and undergoes source-sink evolution in Escherichia coli species.J Bacteriol. 2014 Dec;196(24):4276-84. doi: 10.1128/JB.01972-14. Epub 2014 Sep 29. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 25266386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berg, D. E., N. S. Akopyants, and D. Kersulyte. 1994. Fingerprinting microbial genomes using the RAPD or AP-PCR method. Methods Mol. Cell. Biol. 5:13-24.
-
- Burman, W. J., P. E. Breese, B. E. Murray, K. V. Singh, H. A. Batal, T. D. MacKenzie, J. W. Ogle, M. L. Wilson, R. R. Revers, and P. S. Mehler. 2003. Conventional and molecular epidemiology of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole resistance among urinary Escherichia coli isolates. Am. J. Med. 115:358-364. - PubMed
-
- Burr, M. D., and I. L. Pepper. 1997. Variability in presence-absence scoring of AP PCR fingerprints affects computer matching of bacterial isolates. J. Microbiol. Methods 29:63-68.
-
- Ellsworth, D. L., K. D. Rittenhouse, and R. L. Honeycutt. 1993. Artifactual variation in randomly amplified polymorphic DNA banding patterns. BioTechniques 14:214-217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

