First U.S. report of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Veronaea botryosa in a heart transplant recipient and review of the literature
- PMID: 15184488
- PMCID: PMC427812
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.6.2843-2846.2004
First U.S. report of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Veronaea botryosa in a heart transplant recipient and review of the literature
Abstract
Veronaea botryosa is a rare agent of human phaeohyphomycosis. We describe the first case of subcutaneous disease occurring in the United States, alert clinicians to the second report of a transplant-associated mycosis in a heart transplant recipient, extend the previously defined area of endemicity, and review the literature.
Figures
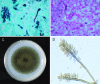
References
-
- Ayadi, A., M. R. Huerre, and C. de Bievre. 1995. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Veronaea bothryosa. Lancet 346:1703-1704. - PubMed
-
- Chabasse, D. 2002. Les phaeohyphomycetes agents de phaeohyphomycosis: des champignons emergents. J. Mycol. Med. 12:65-85.
-
- de Hoog, G. S., J. Guarro, J. Gené, and M. J. Figueras. 2000. Atlas of clinical fungi, 2nd edition. Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures, Utrecht, The Netherlands.
-
- de Hoog, G. S., N. Poonwan, and A. H. G. Gerrits van den Ande. 1999. Taxonomy of Exophiala spinifera and its relationship to E. jeanselmei. Stud. Mycol. 43:133-142.
-
- Ellis, M. B. 1971. Dematiaceous hyphomycetes. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, Farnham Royal, Slough, United Kingdom.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

