CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells dependent on ICOS promote regulation of effector cells in the prediabetic lesion
- PMID: 15184501
- PMCID: PMC2211778
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20040179
CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells dependent on ICOS promote regulation of effector cells in the prediabetic lesion
Abstract
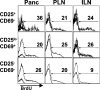
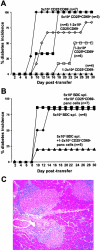
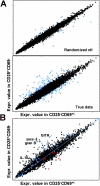
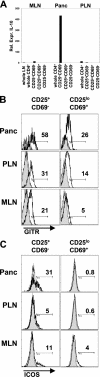
CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells (Tregs) prevent autoimmune disease, yet little is known about precisely where they exert their influence naturally in a spontaneous autoimmune disorder. Here, we report that Tregs and T effector cells (Teffs) coexist within the pancreatic lesion before type 1 diabetes onset. We find that BDC2.5 T cell receptor transgenic animals contain a small subset of FoxP3 positive CD4+CD25+CD69- cells in the pancreas, actively turning over, expressing the clonotypic receptor, and containing functional regulatory activity. Gene expression profiling confirms that the CD4+CD25+CD69- cells in pancreatic tissue express transcripts diagnostic of regulatory cells, but with significantly higher levels of interleukin 10 and inducible costimulator (ICOS) than their lymph node counterparts. Blockade of ICOS rapidly converts early insulitis to diabetes, which disrupts the balance of Teffs and Tregs and promotes a very broad shift in the expression of the T regulatory-specific profile. Thus, CD4+CD25+69- Tregs operate directly in the autoimmune lesion and are dependent on ICOS to keep it in a nondestructive state.
Figures
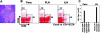

References
-
- Tisch, R., and H. McDevitt. 1996. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Cell. 85:291–297. - PubMed
-
- Lieberman, S.M., A.M. Evans, B. Han, T. Takaki, Y. Vinnitskaya, J.A. Caldwell, D.V. Serreze, J. Shabanowitz, D.F. Hunt, S.G. Nathenson, et al. 2003. Identification of the beta cell antigen targeted by a prevalent population of pathogenic CD8+ T cells in autoimmune diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100:8384–8388. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Katz, J.D., B. Wang, K. Haskins, C. Benoist, and D. Mathis. 1993. Following a diabetogenic T cell from genesis through pathogenesis. Cell. 74:1089–1100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

