The crystal structure of activated protein C-inactivated bovine factor Va: Implications for cofactor function
- PMID: 15184653
- PMCID: PMC428447
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0403072101
The crystal structure of activated protein C-inactivated bovine factor Va: Implications for cofactor function
Abstract
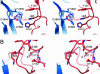
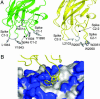
In vertebrate hemostasis, factor Va serves as the cofactor in the prothrombinase complex that results in a 300,000-fold increase in the rate of thrombin generation compared with factor Xa alone. Structurally, little is known about the mechanism by which factor Va alters catalysis within this complex. Here, we report a crystal structure of protein C inactivated factor Va (A1.A3-C1-C2) that depicts a previously uncharacterized domain arrangement. This orientation has implications for binding to membranes essential for function. A high-affinity calcium-binding site and a copper-binding site have both been identified. Surprisingly, neither shows a direct involvement in chain association. This structure represents the largest physiologically relevant fragment of factor Va solved to date and provides a new scaffold for the future generation of models of coagulation cofactors.
Figures



References
-
- Mann, K. G., Butenas, S. & Brummel, K. (2003) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23, 17–25. - PubMed
-
- Nesheim, M. E., Taswell, J. B. & Mann, K. G. (1979) J. Biol. Chem. 254, 10952–10962. - PubMed
-
- Krishnaswamy, S. & Mann, K. G. (1988) J. Biol. Chem. 263, 5714–5723. - PubMed
-
- Nesheim, M. E., Myrmel, K. H., Hibbard, L. S. & Mann, K. G. (1979) J. Biol. Chem. 254, 508–517. - PubMed
-
- Mann, K. G. & Kalafatis, M. (2003) Blood 101, 20–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

