Effective inhibition of Rta expression and lytic replication of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus by human RNase P
- PMID: 15184661
- PMCID: PMC428475
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0403164101
Effective inhibition of Rta expression and lytic replication of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus by human RNase P
Abstract
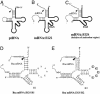
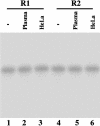
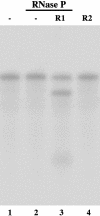
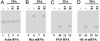
Ribonuclease P (RNase P) complexed with external guide sequence (EGS) represents a nucleic acid-based gene interference approach to knock-down gene expression. Unlike other strategies, such as antisense oligonucleotides, ribozymes, and RNA interference, the RNase P-based technology is unique because a custom-designed EGS molecule can bind to any complementary mRNA sequence and recruit intracellular RNase P for specific degradation of the target mRNA. In this study, we demonstrate that the RNase P-based strategy is effective in blocking gene expression and growth of Kaposi's sarcoma (KS)-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), the causative agent of the leading AIDS-associated neoplasms, such as KS and primary-effusion lymphoma. We constructed 2'-O-methyl-modified EGS molecules that target the mRNA encoding KSHV immediate-early transcription activator Rta, and we administered them directly to human primary-effusion lymphoma cells infected with KSHV. A reduction of 90% in Rta expression and a reduction of approximately 150-fold in viral growth were observed in cells treated with a functional EGS. In contrast, a reduction of <10% in the Rta expression and viral growth was found in cells that were either not treated with an EGS or that were treated with a disabled EGS containing mutations that preclude recognition by RNase P. Our study provides direct evidence that EGSs are highly effective in inhibiting KSHV gene expression and growth. Exogenous administration of chemically modified EGSs in inducing RNase P-mediated cleavage represents an approach for inhibiting specific gene expression and for treating human diseases, including KSHV-associated tumors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Suppressing Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Gene Expression and Replication by RNase P Ribozyme.Molecules. 2023 Apr 21;28(8):3619. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083619. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110852 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of replication and transcription activator and latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus by morpholino oligomers.Antiviral Res. 2007 Jan;73(1):12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2006.05.017. Epub 2006 Jun 14. Antiviral Res. 2007. PMID: 16842866 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) in activation of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic-cycle replication-associated protein (RAP) promoter in cooperation with the KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA) and RAP.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(1):600-23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.1.600-623.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12477864 Free PMC article.
-
[Replication Machinery of Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated Herpesvirus and Drug Discovery Research].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(1):69-73. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00164-2. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30606932 Review. Japanese.
-
Inhibiting KSHV replication by targeting the essential activities of KSHV processivity protein, PF-8.J Med Virol. 2024 Oct;96(10):e29958. doi: 10.1002/jmv.29958. J Med Virol. 2024. PMID: 39370884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of herpes simplex virus 1 gene expression and replication by RNase P-associated external guide sequences.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 9;6:27068. doi: 10.1038/srep27068. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27279482 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered external guide sequences effectively block viral gene expression and replication in cultured cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 7;286(1):322-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.158857. Epub 2010 Oct 27. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 20980254 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered external guide sequences are highly effective in inhibiting gene expression and replication of hepatitis B virus in cultured cells.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 12;8(6):e65268. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065268. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23776459 Free PMC article.
-
RNase P-associated external guide sequence effectively reduces the expression of human CC-chemokine receptor 5 and inhibits the infection of human immunodeficiency virus 1.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:509714. doi: 10.1155/2013/509714. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23509733 Free PMC article.
-
Effective inhibition of cytomegalovirus infection by external guide sequences in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Aug 7;109(32):13070-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201620109. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22826233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang, Y., Cesarman, E., Pessin, M. S., Lee, F., Culpepper, J., Knowles, D. M. & Moore, P. S. (1994) Science 266, 1865-1869. - PubMed
-
- Moore, P. S. & Chang, Y. (2001) in Fields Virology, eds. Knipe, D. M. & Howley, P. M. (Lippincott, Philadelphia), pp. 2803-2834.
-
- Renne, R., Zhong, W., Herndier, B., McGrath, M., Abbey, N., Kedes, D. & Ganem, D. (1996) Nat. Med. 2, 342-346. - PubMed
-
- Boshoff, C., Endo, Y., Collins, P. D., Takeuchi, Y., Reeves, J. D., Schweickart, V. L., Siani, M. A., Sasaki, T., Williams, T. J., Gray, P. W., et al. (1997) Science 278, 290-294. - PubMed
-
- Arvanitakis, L., Geras-Raaka, E., Varma, A., Gershengorn, M. C. & Cesarman, E. (1997) Nature 385, 347-350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

