WR-2721 (Amifostine) ameliorates cisplatin-induced hearing loss but causes neurotoxicity in hamsters: dose-dependent effects
- PMID: 15185124
- PMCID: PMC2504549
- DOI: 10.1007/s10162-004-4011-z
WR-2721 (Amifostine) ameliorates cisplatin-induced hearing loss but causes neurotoxicity in hamsters: dose-dependent effects
Abstract
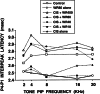
Chemoprotective agents reduce the toxic side effects of chemotherapy agents such as cisplatin. The conventional belief is that the chemoprotective agent WR-2721 (Amifostine), while protecting against most cisplatin-induced side effects, does not protect against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity (i.e., hearing loss). There is no knowledge, however, about the efficacy of high doses of WR-2721 (WR) in possibly protecting against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Thus, the dose-dependent effects of WR in possibly ameliorating cisplatin-induced ototoxicity were investigated. Hamsters were given a series of 5 cisplatin injections (3 mg/kg/injection once every other day, i.p.) either alone or in combination with 18, 40, 80, or 400 mg/kg/injection of the rescue agent WR ( n = 5 or 10/group). Other groups received either 80 mg/kg/injection WR alone ( n = 5) or were untreated ( n = 14). Ototoxicity was assessed by auditory brain stem responses (ABR). WR provided dose-dependent rescue from cisplatin's ototoxicity with no protection at the low dose of 18 mg/kg, moderate protection at 40 mg/kg, and nearly complete protection at 80 and 400 mg/kg. However, WR doses of 40 mg/kg or higher caused neurotoxicity as evidenced by prolongations in the ABR's interpeak latencies. Thus, high doses of WR provided the beneficial effect of protecting against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity, but had the harmful side effect of neurotoxicity. Previous failures to find chemoprotection from cisplatin-induced ototoxicity were likely due to the use of WR doses that were too small. The clinical implications of the beneficial and harmful effects of high doses of WR are discussed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The comparative effects of sodium thiosulfate, diethyldithiocarbamate, fosfomycin and WR-2721 on ameliorating cisplatin-induced ototoxicity.Hear Res. 1995 Jun;86(1-2):195-203. doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(95)00066-d. Hear Res. 1995. PMID: 8567417
-
Comparison of five agents in protecting the cochlea against the ototoxic effects of cisplatin in the hamster.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997 Nov;117(5):493-500. doi: 10.1016/S0194-59989770020-2. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997. PMID: 9374173
-
Assessment of the protective effects of amifostine against cisplatin-induced toxicity.J Otolaryngol. 2003 Oct;32(5):294-7. doi: 10.2310/7070.2003.11264. J Otolaryngol. 2003. PMID: 14974858
-
The potential of amifostine: from cytoprotectant to therapeutic agent.Haematologica. 1999 Nov;84(11):1035-42. Haematologica. 1999. PMID: 10553165 Review.
-
Amifostine for protection from antineoplastic drug toxicity.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1997 Apr 1;54(7):787-800. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/54.7.787. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1997. PMID: 9099346 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of amifostine for protection against cisplatin-induced serious hearing loss in children treated for average-risk or high-risk medulloblastoma.Neuro Oncol. 2014 Jun;16(6):848-55. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not241. Epub 2014 Jan 10. Neuro Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24414535 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Fish Oil Supplementation during the Suckling Period on Auditory Neural Conduction in n-3 Fatty Acid-Deficient Rat Pups.Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2014 Jul;26(76):135-41. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2014. PMID: 25009803 Free PMC article.
-
Amifostine (WR2721) confers DNA protection to in vivo cisplatin-treated murine peripheral blood leukocytes.Dose Response. 2009 Jun 11;7(3):234-46. doi: 10.2203/dose-response.08-026.Prieto. Dose Response. 2009. PMID: 19809542 Free PMC article.
-
Excess omega-3 fatty acid consumption by mothers during pregnancy and lactation caused shorter life span and abnormal ABRs in old adult offspring.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2010 Mar-Apr;32(2):171-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2009.09.006. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2010. PMID: 19818397 Free PMC article.
-
'Ecstasy' enhances noise-induced hearing loss.Hear Res. 2013 Aug;302:96-106. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2013.05.007. Epub 2013 May 25. Hear Res. 2013. PMID: 23711768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blakley BW, Myers SF. Patterns of hearing loss resulting from cis-platinum therapy. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1993;109(3 Pt 1):385–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

