Inhibition of Fas/FasL mRNA expression and TNF-alpha release in concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice by bicyclol
- PMID: 15188504
- PMCID: PMC4572267
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i12.1775
Inhibition of Fas/FasL mRNA expression and TNF-alpha release in concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice by bicyclol
Abstract
Aim: Bicyclol, 4, 4'-dimethoxy-5, 6, 5', 6'-dimethylene-dioxy-2-hydroxymethyl -2'-carbonyl biphenyl, is a new anti-hepatitis drug. The aim of the present study was to investigate the protective effect of bicyclol on concanavalin A (Con A)-induced immunological liver injury in mice and its mechanism.
Methods: Liver injury was induced by injection of Con A via tail vein of mice and assessed biochemically and histologically. Serum transaminase and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) were determined. Liver lesions were observed by light microscope. Expressions of TNF-alpha, interferon gamma (IFN-gamma), Fas and Fas ligand (FasL) mRNA in the livers were measured by RT-PCR.
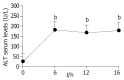
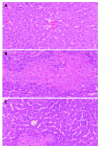
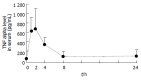
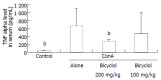
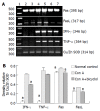
Results: Serum transaminase level and liver lesions in Con A-induced mice were markedly reduced by oral administration of 100, 200 mg/kg of bicyclol. TNF-alpha level in serum was also reduced by bicyclol. Con A injection induced up-regulation of TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma, Fas and FasL mRNA expression in liver tissues. Bicyclol significantly down-regulated the expression of IFN-gamma, Fas and FasL mRNA, but only slightly affected TNF-alpha mRNA expression in liver tissues.
Conclusion: Bicyclol protects against Con A-induced liver injury mainly through inhibition of Fas/FasL mRNA expression in liver tissues and TNF-alpha release in mice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disparate roles for TNF-alpha and Fas ligand in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis.J Immunol. 1998 Apr 15;160(8):4082-9. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9558119
-
The protective action of scutellarin against immunological liver injury induced by concanavalin A and its effect on pro-inflammatory cytokines in mice.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2007 Jan;59(1):115-21. doi: 10.1211/jpp.59.1.0015. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17227628
-
[Effect of ronggan mixture on immunoregulation and hepatocyte apoptosis-related factors in concanavalin A induced acute immunological liver injury mice].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2013 Nov;33(11):1500-6. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24483111 Chinese.
-
Development of real time PCR assays for the quantification of Fas and FasL mRNA levels in lymphocytes: studies on centenarians.Mech Ageing Dev. 2003 Apr;124(4):511-6. doi: 10.1016/s0047-6374(03)00029-0. Mech Ageing Dev. 2003. PMID: 12714260 Review.
-
The mouse interferon-gamma transgene chronic hepatitis model (Review).Int J Mol Med. 1999 May;3(5):517-20. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.3.5.517. Int J Mol Med. 1999. PMID: 10202184 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Bicyclol Tablets on Drug Induced Liver Injuries after Kidney Transplantation.Open Med (Wars). 2017 May 4;12:62-69. doi: 10.1515/med-2017-0012. eCollection 2017. Open Med (Wars). 2017. PMID: 28730164 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A2A receptor activation reduces hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting CD1d-dependent NKT cell activation.J Exp Med. 2006 Nov 27;203(12):2639-48. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061097. Epub 2006 Nov 6. J Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 17088433 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo siRNA delivery of Keap1 modulates death and survival signaling pathways and attenuates concanavalin-A-induced acute liver injury in mice.Dis Model Mech. 2014 Sep;7(9):1093-100. doi: 10.1242/dmm.015537. Epub 2014 Jul 4. Dis Model Mech. 2014. PMID: 24997191 Free PMC article.
-
A novel antihepatitis drug, bicyclol, prevents liver carcinogenesis in diethylnitrosamine-initiated and phenobarbital-promoted mice tumor model.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:584728. doi: 10.1155/2012/584728. Epub 2012 Feb 21. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22500097 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Silymarin, Alone or in Combination with Chlorogenic Acid and/or Melatonin, Against Carbon Tetrachloride-induced Hepatotoxicity.Pharmacogn Mag. 2016 May;12(Suppl 3):S337-45. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.185765. Pharmacogn Mag. 2016. PMID: 27563222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu J, McIntosh H, Lin H. Chinese medicinal herbs for chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review. Liver. 2001;21:280–286. - PubMed
-
- Haria M, Benfield P. Interferon-alpha-2a. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in the management of viral hepatitis. Drugs. 1995;50:873–896. - PubMed
-
- Heathcote J. Treatment of HBe antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. Semin Liver Dis. 2003;23:69–80. - PubMed
-
- Liu GT. The anti-virus and hepatoprotective effect of bicyclol and its mechanism of action. Chin J New Drug Clin. 2001;10:325–327.
-
- Yao GB, Ji YY, Wang QH, Zhou XQ, Xu DZ, Chen XY. A ran-domized double-blind controlled trial of bicyclol in treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Chin J New Drug Clin. 2002;21:457–461.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

