Management of nonfunctioning islet cell tumors
- PMID: 15188511
- PMCID: PMC4572274
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i12.1806
Management of nonfunctioning islet cell tumors
Abstract
Aim: To more clearly define the clinical and pathological characteristics and appropriate diagnosis and treatment of nonfunctioning (NFICTs) islet cell tumors, and to review our institutional experience over the last 30 years.
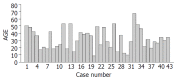
Methods: The records of 43 patients confirmed to have nonfunctioning islet cell tumors of pancreas were retrospectively reviewed. Survival was estimated by the Kaplan-Meier methods and potential risk factors for survival were compared with the log-rank tests.
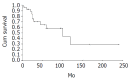
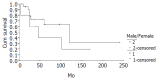
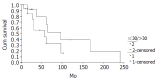
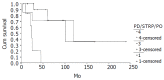
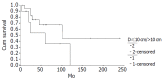
Results: The mean age was 31.63 years (range, 8 to 67 years). There were 7 men and 36 women. Twenty-eight patients had a confirmed diagnosis of nonfunctioning islet cell carcinoma (NFICC) and benign islet cell tumors were found in 15 patients. The most common symptoms in patients with NFICTs were abdominal pain (55.8%), nausea and/or vomiting (32.6%), fatigue (25.6%) and abdominal mass (23.3%). Preoperative ultrasonic and computed tomography localized the tumors in all patients. Forty-three NFICTs were distributed throughout the pancreas, with 21 located to the right of the superior mesenteric vessels, 10 in the body of the pancreas, 6 in the tail of the pancreas, and multiple tumors were found in one patient. Thirty-nine of 43 patients (91%) underwent surgical resection. Surgical treatment was curative in 30 patients (70%) and palliative in 9(21%). The resectability and curative resection rate in patients with NFICC of pancreas were 89% and 61%, respectively. The overall cumulative 5- and 10-year survival rates for patients with NFICC were 58.05% and 29.03%, respectively. Radical operation and diameter of cancer small than 10 cm were positive prognostic factors in females younger than 30 years old. Multivariate Cox regression analysis indicated that radical operation was the only independent prognostic factor, P=0.007.
Conclusion: Nonfunctioning islet cell tumors of pancreas are found mainly in young women. The long-term results for patients undergone surgery, especially curative resection are good.
Figures
References
-
- Broughan TA, Leslie JD, Soto JM, Hermann RE. Pancreatic islet cell tumors. Surgery. 1986;99:671–678. - PubMed
-
- Eriksson B, Skogseid B, Lundqvist G, Wide L, Wilander E, Oberg K. Medical treatment and long-term survival in a prospective study of 84 patients with endocrine pancreatic tumors. Cancer. 1990;65:1883–1890. - PubMed
-
- Bartsch DK, Schilling T, Ramaswamy A, Gerdes B, Celik I, Wagner HJ, Simon B, Rothmund M. Management of nonfunctioning islet cell carcinomas. World J Surg. 2000;24:1418–1424. - PubMed
-
- White TJ, Edney JA, Thompson JS, Karrer FW, Moor BJ. Is there a prognostic difference between functional and nonfunctional islet cell tumors. Am J Surg. 1994;168:627–629; discussion 627-629;. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

