NF-kappaB p50 facilitates neutrophil accumulation during LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation
- PMID: 15189567
- PMCID: PMC449706
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-5-10
NF-kappaB p50 facilitates neutrophil accumulation during LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation
Abstract
Background: Transcription factors have distinct functions in regulating immune responses. During Escherichia coli pneumonia, deficiency of NF-kappaB p50 increases gene expression and neutrophil recruitment, suggesting that p50 normally limits these innate immune responses. p50-deficient mice were used to determine how p50 regulates responses to a simpler, non-viable bacterial stimulus in the lungs, E. coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
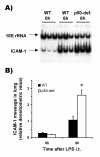
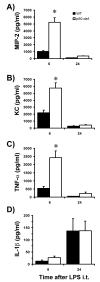
Results: In contrast to previous results with living E. coli, neutrophil accumulation elicited by E. coli LPS in the lungs was decreased by p50 deficiency, to approximately 30% of wild type levels. Heat-killed E. coli induced neutrophil accumulation which was not decreased by p50 deficiency, demonstrating that bacterial growth and metabolism were not responsible for the different responses to bacteria and LPS. p50 deficiency increased the LPS-induced expression of kappaB-regulated genes essential to neutrophil recruitment, including KC, MIP-2, ICAM-1, and TNF-alpha suggesting that p50 normally limited this gene expression and that decreased neutrophil recruitment did not result from insufficient expression of these genes. Neutrophils were responsive to the chemokine KC in the peripheral blood of p50-deficient mice with or without LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation. Interleukin-6 (IL-6), previously demonstrated to decrease LPS-induced neutrophil recruitment in the lungs, was increased by p50 deficiency, but LPS-induced neutrophil recruitment was decreased by p50 deficiency even in IL-6 deficient mice.
Conclusion: p50 makes essential contributions to neutrophil accumulation elicited by LPS in the lungs. This p50-dependent pathway for neutrophil accumulation can be overcome by bacterial products other than LPS and does not require IL-6.
Figures


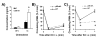
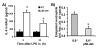
References
-
- Frevert CW, Huang S, Danaee H, Paulauskis JD, Kobzik L. Functional characterization of the rat chemokine KC and its importance in neutrophil recruitment in a rat model of pulmonary inflammation. J Immunol. 1995;154:335–344. - PubMed
-
- Greenberger MJ, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL, Danforth JM, Laichalk LL, McGillicuddy DC, Standiford TJ. Neutralization of macrophage inflammatory protein-2 attenuates neutrophil recruitment and bacterial clearance in murine Klebsiella pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 1996;173:159–165. - PubMed
-
- Schmal H, Shanley TP, Jones ML, Friedl HP, Ward PA. Role for macrophage inflammatory protein-2 in lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in rats. J Immunol. 1996;156:1963–1972. - PubMed
-
- Burns AB, Takei F, Doerschuk CM. Quantitation of ICAM-1 expression in mouse lung during pneumonia. J Immunol. 1994;153:3189–3198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

