Infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy of amphipathic model peptides at the air/water interface
- PMID: 15189871
- PMCID: PMC1304276
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.103.035964
Infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy of amphipathic model peptides at the air/water interface
Abstract
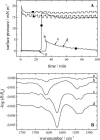
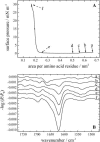
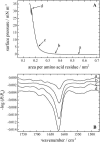
The linear sequence KLAL (KLALKLALKALKAALKLA-NH(2)) and its corresponding d,l-isomers k(9)a(10)-KLAL (KLALKLALkaLKAALKLA-NH(2)) and l(11)k(12)-KLAL (KLALKLALKAlkAALKLA-NH(2)) are model compounds for potentially amphipathic alpha-helical peptides which are able to bind to membranes and to increase the membrane permeability in a structure- and target-dependent manner (Dathe and Wieprecht, 1999) We first studied the secondary structure of KLAL and its analogs bound to the air/water using infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy. For the peptide films the shape and position of the amide I and amide II bands indicate that the KLAL adopts at large areas per molecule an alpha-helical secondary structure, whereas at higher surface pressures or smaller areas it converts into a beta-sheet structure. This transition could be observed in the compression isotherm as well as during the adsorption at the air/water interface from the subphase as a function of time. The secondary structures are essentially orientated parallel to the air/water interface. The analogs with d-amino acids in two different positions of the sequence, k(9)a(10)-KLAL and l(11)k(12)-KLAL, form only beta-sheet structures at all surface pressures. The observed results are interpreted using a comparison of hydrophobic moments calculated for alpha-helices and beta-sheets. The differences between the hydrophobic moments calculated using the consensus scale are not large. Using the optimal matching hydrophobicity scale or the whole-residue hydrophobicity scale the beta-sheet even has the larger hydrophobic moment.
Figures



References
-
- Andreu, D., and L. Rivas. 1998. Animal antimicrobial peptides: an overview. Biopolymers. 47:415–433. - PubMed
-
- Bechinger, B. 1999. The structure, dynamics and orientation of antimicrobial peptides in membranes by multidimensional solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1462:157–183. - PubMed
-
- Blaudez, D., J.-M. Turlet, J. Dufourcq, D. Bard, T. Buffeteau, and B. Desbat. 1996. Investigations at the air/water interface using polarization modulation IR spectroscopy. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 92:525–530.
-
- Castano, S., I. Cornut, K. Büttner, J. L. Dasseux, and J. Dufourcq. 1999a. The amphipathic helix concept: length effects on ideally amphipathic LiKj(i = 2j) peptides to acquire optimal hemolytic activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1416:161–175. - PubMed
-
- Castano, S., B. Desbat, I. Cornut, P. Meleard, and J. Dufourcq. 1997. α-Helix to β-sheet transition within the LeuiLysj (i = 2j) series of lytic amphipathic peptides by decreasing their size. Lett. Peptide Sci. 4:195–200.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

