Beta-1 integrin-mediated adhesion may be initiated by multiple incomplete bonds, thus accounting for the functional importance of receptor clustering
- PMID: 15189901
- PMCID: PMC1304306
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.103.038778
Beta-1 integrin-mediated adhesion may be initiated by multiple incomplete bonds, thus accounting for the functional importance of receptor clustering
Abstract
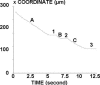
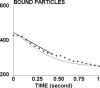
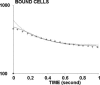
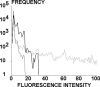
The regulation of cell integrin receptors involves modulation of membrane expression, shift between different affinity states, and topographical redistribution on the cell membrane. Here we attempted to assess quantitatively the functional importance of receptor clustering. We studied beta-1 integrin-mediated attachment of THP-1 cells to fibronectin-coated surfaces under low shear flow. Cells displayed multiple binding events with a half-life of the order of 1 s. The duration of binding events after the first second after arrest was quantitatively accounted for by a model assuming the existence of a short-time intermediate binding state with 3.6 s(-1) dissociation rate and 1.3 s(-1) transition frequency toward a more stable state. Cell binding to surfaces coated with lower fibronectin densities was concluded to be mediated by single molecular interactions, whereas multiple bonds were formed <1 s after contact with higher fibronectin surface densities. Cell treatment with microfilament inhibitors or a neutral antiintegrin antibody decreased bond number without changing aforementioned kinetic parameters whereas a function enhancing antibody increased the rate of bond formation and/or the lifetime of intermediate state. Receptor aggregation was induced by treating cells with neutral antiintegrin antibody and antiimmunoglobulin antibodies. A semiquantitative confocal microscopy study suggested that this treatment increased between 40% and 100% the average number of integrin receptors located in a volume of approximately 0.045 microm(3) surrounding each integrin. This aggregation induced up to 2.7-fold increase of the average number of bonds. Flow cytometric analysis of fluorescent ligand binding showed that THP-1 cells displayed low-affinity beta-1 integrins with a dissociation constant in the micromolar range. It is concluded that the initial step of cell adhesion was mediated by multiple incomplete bonds rather than a single equilibrium-state ligand receptor association. This interpretation accounts for the functional importance of integrin clustering.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Integrins in cell adhesion and signaling.Hum Cell. 1996 Sep;9(3):181-6. Hum Cell. 1996. PMID: 9183647 Review.
-
Differential cation regulation of the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin-mediated adhesion of leukemic cells to the central cell-binding domain of fibronectin.Cell Growth Differ. 1997 Dec;8(12):1339-47. Cell Growth Differ. 1997. PMID: 9419422
-
Regulation of integrin-mediated adhesion at focal contacts by cyclic AMP.J Cell Physiol. 1993 Nov;157(2):296-306. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041570212. J Cell Physiol. 1993. PMID: 7693723
-
Adhesion of neutrophils to fibronectin: role of the cd66 antigens.Cell Immunol. 2001 Mar 15;208(2):96-106. doi: 10.1006/cimm.2001.1772. Cell Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11333142
-
Morphology of cell-substratum adhesion. Influence of receptor heterogeneity and nonspecific forces.Cell Biophys. 1992 Apr-Jun;20(2-3):177-222. doi: 10.1007/BF02823657. Cell Biophys. 1992. PMID: 1285299 Review.
Cited by
-
Two-dimensional kinetics regulation of alphaLbeta2-ICAM-1 interaction by conformational changes of the alphaL-inserted domain.J Biol Chem. 2005 Dec 23;280(51):42207-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510407200. Epub 2005 Oct 18. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16234238 Free PMC article.
-
A computational analysis of the role of integrins and Rho-GTPases in the emergence and disruption of apical-basal polarization in renal epithelial cells.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 May 20;20(5):e1012140. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012140. eCollection 2024 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 38768266 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of receptor clustering on ligand binding.BMC Syst Biol. 2011 Mar 31;5:48. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-5-48. BMC Syst Biol. 2011. PMID: 21453460 Free PMC article.
-
Studying Molecular Interactions at the Single Bond Level with a Laminar Flow Chamber.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2008 Dec;1(4):247-262. doi: 10.1007/s12195-008-0031-9. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2008. PMID: 21151952 Free PMC article.
-
A spatial model for integrin clustering as a result of feedback between integrin activation and integrin binding.Biophys J. 2012 Sep 19;103(6):1379-89. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.08.021. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 22995511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alon, R., D. A. Hammer, and T. A. Springer. 1995. Lifetime of P-selectin-carbohydrate bond and its response to tensile force in hydrodynamic flow. Nature. 374:539–542. - PubMed
-
- André, P., A. M. Benoliel, C. Capo, C. Foa, M. Buferne, C. Boyer, A. M. Schmitt-Verhulst, and P. Bongrand. 1990. Use of conjugates made between a cytolytic T cell clone and target cells to study the redistribution of membrane molecules in contact areas. J. Cell Sci. 97:335–347. - PubMed
-
- Cai, T. Q., and S. D. Wright. 1995. Energetics of leukocyte integrin activation. J. Biol. Chem. 270:14358–14365. - PubMed
-
- Chen, L. L., A. Whitty, R. R. Lobb, S. P. Adams, and R. B. Pepinsky. 1999. Multiple activation states of integrin alpha 4 - beta 1 detected through their different affinities for a small molecule ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 274:13167–13175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

