SYM1 is the stress-induced Saccharomyces cerevisiae ortholog of the mammalian kidney disease gene Mpv17 and is required for ethanol metabolism and tolerance during heat shock
- PMID: 15189984
- PMCID: PMC420134
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.3.3.620-631.2004
SYM1 is the stress-induced Saccharomyces cerevisiae ortholog of the mammalian kidney disease gene Mpv17 and is required for ethanol metabolism and tolerance during heat shock
Abstract
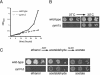
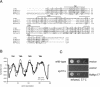
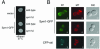
Organisms rapidly adapt to severe environmental stress by inducing the expression of a wide array of heat shock proteins as part of a larger cellular response program. We have used a genomics approach to identify novel heat shock-induced genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The uncharacterized open reading frame (ORF) YLR251W was found to be required for both metabolism and tolerance of ethanol during heat shock. YLR251W has significant homology to the mammalian peroxisomal membrane protein Mpv17, and Mpv17(-/-) mice exhibit age-onset glomerulosclerosis, deafness, hypertension, and, ultimately, death by renal failure. Expression of Mpv17 in ylr251wdelta cells complements the 37 degrees C ethanol growth defect, suggesting that these proteins are functional orthologs. We have therefore renamed ORF YLR251W as SYM1 (for "stress-inducible yeast Mpv17"). In contrast to the peroxisomal localization of Mpv17, we find that Sym1 is an integral membrane protein of the inner mitochondrial membrane. In addition, transcriptional profiling of sym1delta cells uncovered changes in gene expression, including dysregulation of a number of ethanol-repressed genes, exclusively at 37 degrees C relative to wild-type results. Together, these data suggest an important metabolic role for Sym1 in mitochondrial function during heat shock. Furthermore, this study establishes Sym1 as a potential model for understanding the role of Mpv17 in kidney disease and cardiovascular biology.
Copyright 2004 American Society for Microbiology
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pathological alleles of MPV17 modeled in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae orthologous gene SYM1 reveal their inability to take part in a high molecular weight complex.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 1;13(10):e0205014. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205014. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30273399 Free PMC article.
-
Sym1, the yeast ortholog of the MPV17 human disease protein, is a stress-induced bioenergetic and morphogenetic mitochondrial modulator.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Mar 15;19(6):1098-107. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp581. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2010. PMID: 20042463
-
Methylglyoxal-mediated Gpd1 activation restores the mitochondrial defects in a yeast model of mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2023 May;1867(5):130328. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2023.130328. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2023. PMID: 36791826
-
The role of the Mpv17 protein mutations of which cause mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome (MDDS): lessons from homologs in different species.Biol Chem. 2015 Jan;396(1):13-25. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2014-0198. Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25205723 Review.
-
The heat shock and ethanol stress responses of yeast exhibit extensive similarity and functional overlap.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995 Dec 15;134(2-3):121-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1995.tb07925.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995. PMID: 8586257 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug Drop Test: How to Quickly Identify Potential Therapeutic Compounds for Mitochondrial Diseases Using Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 27;24(13):10696. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310696. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salt stress perception and metabolic regulation network analysis of a marine probiotic Meyerozyma guilliermondii GXDK6.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jul 17;14:1193352. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1193352. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37529325 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast as a system for modeling mitochondrial disease mechanisms and discovering therapies.Dis Model Mech. 2015 Jun;8(6):509-26. doi: 10.1242/dmm.020438. Dis Model Mech. 2015. PMID: 26035862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological alleles of MPV17 modeled in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae orthologous gene SYM1 reveal their inability to take part in a high molecular weight complex.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 1;13(10):e0205014. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205014. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30273399 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression mutants reveal a role for a chloroplast MPD protein in regulation of reactive oxygen species during chilling in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2022 Apr 18;73(8):2666-2681. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac029. J Exp Bot. 2022. PMID: 35084440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilera, A., and T. Benitez. 1986. Ethanol-sensitive mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch. Microbiol. 143:337-344. - PubMed
-
- Aguilera, A., and T. Benitez. 1985. Role of mitochondria in ethanol tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch. Microbiol. 142:389-392. - PubMed
-
- Binder, C. J., H. Weiher, M. Exner, and D. Kerjaschki. 1999. Glomerular overproduction of oxygen radicals in mpv17 gene-inactivated mice causes podocyte foot process flattening and proteinuria: a model of steroid-resistant nephrosis sensitive to radical scavenger therapy. Am. J. Pathol. 154:1067-1075. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blachly-Dyson, E., S. Peng, M. Colombini, and M. Forte. 1990. Selectivity changes in site-directed mutants of the VDAC ion channel: structural implications. Science 247:1233-1236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

