The Gbeta-subunit-encoding gene bpp1 controls cyclic-AMP signaling in Ustilago maydis
- PMID: 15190001
- PMCID: PMC420130
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.3.3.806-814.2004
The Gbeta-subunit-encoding gene bpp1 controls cyclic-AMP signaling in Ustilago maydis
Abstract
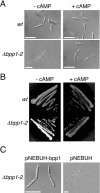
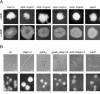
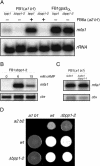
In the phytopathogenic fungus Ustilago maydis, fusion of haploid cells is a prerequisite for infection. This process is controlled by a pheromone-receptor system. The receptors belong to the seven-transmembrane class that are coupled to heterotrimeric G proteins. Of four Galpha subunits in U. maydis, only gpa3 has a function during mating and cyclic AMP (cAMP) signaling. Activation of the cAMP cascade induces pheromone gene expression; however, it does not lead to the induction of conjugation tubes seen after pheromone stimulation. To investigate the possibility that a Gbeta subunit participates in pheromone signaling, we isolated the single beta subunit gene, bpp1, from U. maydis. bpp1 deletion mutants grew filamentously and showed attenuated pheromone gene expression, phenotypes associated with deltagpa3 strains. In addition, a constitutively active allele of gpa3 suppressed the phenotype of the bpp1 deletion strains. We suggest that Bpp1 and Gpa3 are components of the same heterotrimeric G protein acting on adenylyl cyclase. Interestingly, while deltagpa3 strains are impaired in pathogenicity, deltabpp1 mutants are able to induce plant tumors. This could indicate that Gpa3 operates independently of Bpp1 during pathogenic development.
Copyright 2004 American Society for Microbiology
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crosstalk between cAMP and pheromone signalling pathways in Ustilago maydis.Mol Gen Genet. 1998 Nov;260(2-3):193-8. doi: 10.1007/s004380050885. Mol Gen Genet. 1998. PMID: 9862471
-
G proteins in Ustilago maydis: transmission of multiple signals?EMBO J. 1997 Apr 15;16(8):1934-42. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.8.1934. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9155019 Free PMC article.
-
Guanyl nucleotide exchange factor Sql2 and Ras2 regulate filamentous growth in Ustilago maydis.Eukaryot Cell. 2003 Jun;2(3):609-17. doi: 10.1128/EC.2.3.609-617.2003. Eukaryot Cell. 2003. PMID: 12796306 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of morphogenesis and pathogenic development of Ustilago maydis.Adv Genet. 2007;57:1-47. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2660(06)57001-4. Adv Genet. 2007. PMID: 17352901 Review.
-
Regulation of mating and pathogenic development in Ustilago maydis.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2004 Dec;7(6):666-72. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2004.10.006. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15556041 Review.
Cited by
-
Basidiomycete mating type genes and pheromone signaling.Eukaryot Cell. 2010 Jun;9(6):847-59. doi: 10.1128/EC.00319-09. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Eukaryot Cell. 2010. PMID: 20190072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The late endosomal HOPS complex anchors active G-protein signaling essential for pathogenesis in magnaporthe oryzae.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(8):e1003527. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003527. Epub 2013 Aug 1. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23935502 Free PMC article.
-
G(alpha) and Gbeta proteins regulate the cyclic AMP pathway that is required for development and pathogenicity of the phytopathogen Mycosphaerella graminicola.Eukaryot Cell. 2009 Jul;8(7):1001-13. doi: 10.1128/EC.00258-08. Epub 2009 May 1. Eukaryot Cell. 2009. PMID: 19411619 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple roles of a heterotrimeric G-protein gamma-subunit in governing growth and development of Aspergillus nidulans.Genetics. 2005 Sep;171(1):81-9. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.042796. Epub 2005 Jun 8. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15944346 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion of Signal Transduction Pathways in Fungi by Extensive Genome Duplication.Curr Biol. 2016 Jun 20;26(12):1577-1584. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.04.038. Epub 2016 May 26. Curr Biol. 2016. PMID: 27238284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews, D. L., J. D. Egan, M. E. Mayorga, and S. E. Gold. 2000. The Ustilago maydis ubc4 and ubc5 genes encode members of a MAP kinase cascade required for filamentous growth. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 13:781-786. - PubMed
-
- Banuett, F. 1992. Ustilago maydis, the delightful blight. Trends Genet. 8:174-180. - PubMed
-
- Banuett, F., and I. Herskowitz. 1994. Identification of fuz7, a Ustilago maydis MEK/MAPKK homolog required for a-locus-dependent and -independent steps in the fungal life cycle. Genes Dev. 8:1367-1378. - PubMed
-
- Barrett, K. J., S. E. Gold, and J. W. Kronstad. 1993. Identification and complementation of a mutation to constitutive filamentous growth in Ustilago maydis. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 6:274-283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

