Microdomains for dopamine volume neurotransmission in primate prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 15190100
- PMCID: PMC6729299
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0195-04.2004
Microdomains for dopamine volume neurotransmission in primate prefrontal cortex
Abstract
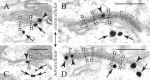
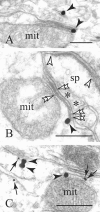
The explicit yet enigmatic involvement of dopamine in cortical physiology is in part volumetric (beyond the synapse), as is apparently the action of neuroleptics targeting dopamine receptors. The notion that nonsynaptic neuronal membranes would translate extracellular dopamine into receptor-specific spatiotemporal downstream signaling, similar to the chemical synapse, is intriguing. Here, we report that dopamine D5 (but not D1 or D2) receptors in the perisomatic plasma membrane of prefrontal cortical neurons form discrete and exclusively extrasynaptic microdomains with inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-gated calcium stores of subsurface cisterns and mitochondria. These findings introduce a novel dopaminoceptive substratum in the brain and a unique D5 receptor-specific signaling paradigm.
Figures





References
-
- Agnati LF, Bjelke B, Fuxe K (1995a) Volume versus wiring transmission in the brain: a new theoretical frame for neuropsychopharmacology. Med Res Rev 15: 33-45. - PubMed
-
- Agnati LF, Zoli M, Strömberg I, Fuxe K (1995b) Intercellular communication in the brain: wiring versus volume transmission. Neuroscience 69: 711-726. - PubMed
-
- Agnati LF, Fuxe K, Nicholson C, Syková E (2000) Progress in brain research, Vol 125. Volume transmission revisited. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
-
- Alonso-Nanclares L, Minelli A, Melone M, Edwards RH, DeFelipe J, Conti F (2004) Perisomatic glutamatergic axon terminals: a novel feature of cortical synaptology revealed by vesicular glutamate transporter 1 immunostaining. Neuroscience 123: 547-556. - PubMed
-
- Ariano MA, Wang J, Noblett KL, Larson ER, Sibley DR (1997) Cellular distribution of the rat D1B receptor in central nervous system using anti-receptor antisera. Brain Res 746: 141-150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
