Catechol-o-methyltransferase inhibition improves set-shifting performance and elevates stimulated dopamine release in the rat prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 15190105
- PMCID: PMC6729311
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1124-04.2004
Catechol-o-methyltransferase inhibition improves set-shifting performance and elevates stimulated dopamine release in the rat prefrontal cortex
Abstract
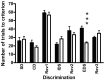
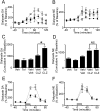
The Val158Met polymorphism of the human catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) gene affects activity of the enzyme and influences performance and efficiency of the prefrontal cortex (PFC); however, although catecholaminergic neurotransmission is implicated, the underlying mechanisms remain elusive because studies of the role of COMT in PFC function are sparse. This study investigated the effect of tolcapone, a brain-penetrant COMT inhibitor, on a rat model of attentional set shifting, which is dependent on catecholamines and the medial PFC (mPFC). Additionally, we investigated the effect of tolcapone on extracellular catecholamines in the mPFC using microdialysis in awake rats. Tolcapone significantly and specifically improved extradimensional (ED) set shifting. Tolcapone did not affect basal extracellular catecholamines, but significantly potentiated the increase in extracellular dopamine (DA) elicited by either local administration of the depolarizing agent potassium chloride or systemic administration of the antipsychotic agent clozapine. Although extracellular norepinephrine (NE) was also elevated by local depolarization and clozapine, the increase was not enhanced by tolcapone. We conclude that COMT activity specifically affects ED set shifting and is a significant modulator of mPFC DA but not NE under conditions of increased catecholaminergic transmission. These data suggest that the links between COMT activity and PFC function can be modeled in rats and may be specifically mediated by DA. The interaction between clozapine and tolcapone may have implications for the treatment of schizophrenia.
Figures
References
-
- Acquas E, Carboni E, de Ree RHA, Da Prada M, Di Chiara G (1992) Extra-cellular concentrations of dopamine and metabolites in the rat caudate after oral administration of a novel catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor Ro 40-7592. J Neurochem 59: 326-330. - PubMed
-
- Bertolino A, Caforio G, Blasi G, De Candia M, Latorre V, Petruzzella V, Altamura M, Nappi G, Papa S, Callicot JH, Mattay VS, Bellomo A, Scarabino T, Weinberger DR, Nardini M (2003) Differential effect of COMT Val108/158 Met genotype on enhancement of prefrontal cortical function and working memory in patients with schizophrenia treated with olanzapine. Soc Neurosci Abstr 29: 881.5.
-
- Ceravolo R, Piccini P, Bailey DL, Jorga KM, Bryson H, Brooks DJ (2002) 18F-Dopa PET evidence that tolcapone acts as a central COMT inhibitor in Parkinson's disease. Synapse 43: 201-207. - PubMed
-
- Crofts HS, Dalley JW, Collins P, Van Denderen JCM, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW, Roberts AC (2001) Differential effect of 6-OHDA lesions of the frontal cortex and caudate nucleus on the ability to acquire an attentional set. Cereb Cortex 11: 1015-1026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
