Identification of sympathetic premotor neurons in medullary raphe regions mediating fever and other thermoregulatory functions
- PMID: 15190110
- PMCID: PMC6729310
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1219-04.2004
Identification of sympathetic premotor neurons in medullary raphe regions mediating fever and other thermoregulatory functions
Abstract
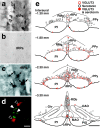
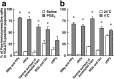
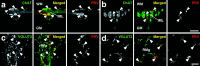
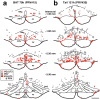
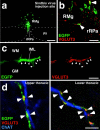
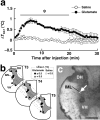
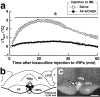
Sympathetic premotor neurons directly control sympathetic preganglionic neurons (SPNs) in the intermediolateral cell column (IML) of the thoracic spinal cord, and many of these premotor neurons are localized in the medulla oblongata. The rostral ventrolateral medulla contains premotor neurons controlling the cardiovascular conditions, whereas rostral medullary raphe regions are a candidate source of sympathetic premotor neurons for thermoregulatory functions. Here, we show that these medullary raphe regions contain putative glutamatergic neurons and that these neurons directly control thermoregulatory SPNs. Neurons expressing vesicular glutamate transporter 3 (VGLUT3) were distributed in the rat medullary raphe regions, including the raphe magnus and rostral raphe pallidus nuclei, and mostly lacked serotonin immunoreactivity. These VGLUT3-positive neurons expressed Fos in response to cold exposure or to central administration of prostaglandin E2, a pyrogenic mediator. Transneuronal retrograde labeling after inoculation of pseudorabies virus into the interscapular brown adipose tissue (BAT) or the tail indicated that those VGLUT3-expressing medullary raphe neurons innervated these thermoregulatory effector organs multisynaptically through SPNs of specific thoracic segments, and microinjection of glutamate into the IML of the BAT-controlling segments produced BAT thermogenesis. An anterograde tracing study further showed a direct projection of those VGLUT3-expressing medullary raphe neurons to the dendrites of SPNs. Furthermore, intra-IML application of glutamate receptor antagonists blocked BAT thermogenesis triggered by disinhibition of the medullary raphe regions. The present results suggest that VGLUT3-expressing neurons in the medullary raphe regions constitute excitatory neurons that could be categorized as a novel group of sympathetic premotor neurons for thermoregulatory functions, including fever.
Figures

References
-
- Aicher SA, Hahn B-I, Milner TA (2000) N-methyl-d-aspartate-type glutamate receptors are found in post-synaptic targets of adrenergic terminals in the thoracic spinal cord. Brain Res 856: 1-11. - PubMed
-
- Bamshad M, Song CK, Bartness TJ (1999) CNS origins of the sympathetic nervous system outflow to brown adipose tissue. Am J Physiol 276: R1569-R1578. - PubMed
-
- Blessing WW, Nalivaiko E (2001) Raphe magnus/pallidus neurons regulate tail but not mesenteric arterial blood flow in rats. Neuroscience 105: 923-929. - PubMed
-
- Blessing WW, Yu YH, Nalivaiko E (1999) Raphe pallidus and parapyramidal neurons regulate ear pinna vascular conductance in the rabbit. Neurosci Lett 270: 33-36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
