Phospholipases C and A2 control lysosome-mediated IL-1 beta secretion: Implications for inflammatory processes
- PMID: 15192144
- PMCID: PMC470745
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0308558101
Phospholipases C and A2 control lysosome-mediated IL-1 beta secretion: Implications for inflammatory processes
Abstract
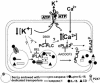
Blocking the activity of IL-1 beta has entered the clinical arena of treating autoimmune diseases. However, a successful outcome of this approach requires a clear definition of the mechanisms controlling IL-1 beta release. These are still unclear as IL-1 beta, lacking a secretory signal peptide, follows a nonclassical pathway of secretion. Here, we analyze the molecular mechanism(s) undergoing IL-1 beta processing and release in human monocytes and provide a unifying model for the regulated secretion of the cytokine. Our data show that in a first step, pro-caspase-1 and endotoxin-induced pro-IL-1 beta are targeted in part to specialized secretory lysosomes, where they colocalize with other lysosomal proteins. Externalization of mature IL-1 beta and caspase-1 together with lysosomal proteins is then facilitated by extracellular ATP. ATP triggers the efflux of K(+) from the cell, followed by Ca(2+) influx and activation of three phospholipases: phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C and calcium-independent and -dependent phospholipase A(2). Whereas calcium-independent phospholipase A(2) is involved in processing, phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C and calcium-dependent phospholipase A(2) are required for secretion. Dissection of the events that follow ATP triggering allowed to demonstrate that K(+) efflux is responsible for phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C induction, which in turn allows the rise in intracellular free calcium concentration required for activation of phospholipase A(2). This activation is ultimately responsible for lysosome exocytosis and IL-1 beta secretion.
Figures
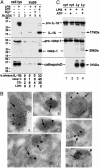
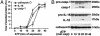
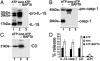


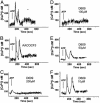
Comment in
-
IL-1beta: an endosomal exit.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jul 13;101(28):10241-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403971101. Epub 2004 Jul 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15240873 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dinarello, C. A. (1998) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 856, 1-11. - PubMed
-
- Rubartelli, A. & Sitia, R. (1997) in Unusual Secretory Pathways: From Bacteria to Man, eds. Kuchler, K., Rubartelli, A. & Holland, B. I. (RG Landes, Austin, TX), pp. 87-104.
-
- Burns, K., Martinon, F. & Tschopp, J. (2003) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 15, 26-30. - PubMed
-
- Perregaux, D. & Gabel. C. A. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269, 15195-15203. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari, D., Chiozzi, P., Falzoni, S., Dal Susino, M., Melchiorri, L., Baricordi, O. R. & Di Virgilio, F. (1997) J. Immunol. 159, 1451-1458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

