Electrotonic coupling between stratum oriens interneurones in the intact in vitro mouse juvenile hippocampus
- PMID: 15194737
- PMCID: PMC1665026
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.065649
Electrotonic coupling between stratum oriens interneurones in the intact in vitro mouse juvenile hippocampus
Abstract
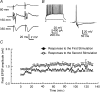
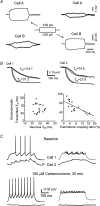
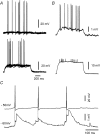
Using the isolated juvenile (7-14 days) mouse whole hippocampus preparation, which contains intact complex local circuitry, 145 dual whole cell recordings were made from stratum oriens (s.o.) interneurones under infrared microscopy. In 11.7% of paired recordings, evidence for direct electrotonic coupling between the s.o. interneurones was obtained from the response of one interneurone to a long (400-600 ms) constant current pulse passed into the coupled interneurone. When specifically orienting the dual recordings in the transectional plane of the hippocampus, 18.5% of paired recordings showed electrotonic coupling. The coupling coefficient, estimated from averaged data, was 6.9 +/- 4.7%, ranging from 1.3 to 17.6%. The time constant of the electrotonically transmitted hyperpolarization was inversely related to the coupling coefficient between the two neurones. The electrotonic responses of one neurone to constant current pulses injected into the other coupled neurone were intermittent. Spikes in one of the coupled neurones were associated with small electrotonic EPSPs (spikelets) in the other coupled neurone, in those neuronal pairs with coupling coefficients greater than 10%. Failure of spikelet production following a spike in the coupled cell occurred 5-10% of the time. Electrotonic coupling and spikelets persisted in the presence of chemical synaptic transmission blockade by CNQX, APV and bicuculline, or in zero Ca(2+) perfusate, but were abolished by carbenoxolone (100 microm), a gap junctional blocker. These data confirm the existence of electrotonic coupling between s.o. interneurones, presumably via gap junctions located in dendrites.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Use-dependent shift from inhibitory to excitatory GABAA receptor action in SP-O interneurons in the rat hippocampal CA3 area.J Neurophysiol. 2003 Sep;90(3):1983-95. doi: 10.1152/jn.00060.2003. Epub 2003 May 15. J Neurophysiol. 2003. PMID: 12750426
-
Heterogeneous electrotonic coupling and synchronization of rhythmic bursting activity in mouse Hb9 interneurons.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Oct;98(4):2370-81. doi: 10.1152/jn.00338.2007. Epub 2007 Aug 22. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17715199
-
Properties of horizontal axo-axonic cells in stratum oriens of the hippocampal CA1 area of rats in vitro.Hippocampus. 2004;14(2):232-43. doi: 10.1002/hipo.10170. Hippocampus. 2004. PMID: 15098728
-
Electrotonic coupling between rat sympathetic preganglionic neurones in vitro.J Physiol. 1996 Sep 1;495 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):491-502. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021609. J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8887759 Free PMC article.
-
Stratum oriens horizontal interneurone diversity and hippocampal network dynamics.J Physiol. 2005 Jan 1;562(Pt 1):73-80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.077081. Epub 2004 Oct 21. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15498801 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Propagation of postsynaptic currents and potentials via gap junctions in GABAergic networks of the rat hippocampus.J Physiol. 2007 Jan 15;578(Pt 2):527-44. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.123463. Epub 2006 Nov 16. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17110410 Free PMC article.
-
Slow periodic activity in the longitudinal hippocampal slice can self-propagate non-synaptically by a mechanism consistent with ephaptic coupling.J Physiol. 2019 Jan;597(1):249-269. doi: 10.1113/JP276904. Epub 2018 Nov 10. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30295923 Free PMC article.
-
Transition to seizure: ictal discharge is preceded by exhausted presynaptic GABA release in the hippocampal CA3 region.J Neurosci. 2012 Feb 15;32(7):2499-512. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4247-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22396423 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical coupling between interneurons with different excitable properties in the stratum lacunosum-moleculare of the juvenile CA1 rat hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2005 Sep 21;25(38):8686-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2810-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16177037 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal regulation of epileptiform neuronal oscillations and electrical synapses in the rat hippocampus.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 9;9(10):e109149. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109149. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25299405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acsady L, Gorcs TJ, Freund TF. Different populations of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-immunoreactive interneurons are specialized to control pyramidal cells or interneurons in the hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1996;73:317–334. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MV. Gap junctions as electrical synapses. J Neurocytol. 1997;26:349–366. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MV. Electrical synapses, a personal perspective (or history) Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000a;32:16–28. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MV. Seeing is relieving: electrical synapses between visualized neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2000b;3:7–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

