Heterogeneous expression of repolarizing, voltage-gated K+ currents in adult mouse ventricles
- PMID: 15194740
- PMCID: PMC1665075
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.063347
Heterogeneous expression of repolarizing, voltage-gated K+ currents in adult mouse ventricles
Erratum in
- J Physiol. 2004 Sep 15;559(Pt 3):985
Abstract
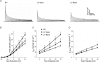
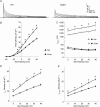
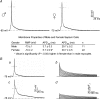
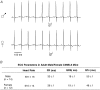
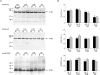
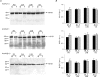
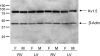
Previous studies have documented the expression of four kinetically distinct voltage-gated K(+) (Kv) currents, I(to,f), I(to,s), I(K,slow) and I(ss), in mouse ventricular myocytes and demonstrated that I(to,f) and I(to,s) are differentially expressed in the left ventricular apex and the interventricular septum. The experiments here were undertaken to test the hypothesis that there are further regional differences in the expression of Kv currents or the Kv subunits (Kv4.2, Kv4.3, KChIP2, Kv1.5, Kv2.1) encoding these currents in adult male and female (C57BL6) mouse ventricles. Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings revealed that mean (+/-s.e.m.) peak outward K(+) current and I(to,f) densities are significantly (P < 0.001) higher in cells isolated from the right (RV) than the left (LV) ventricles. Within the LV, peak outward K(+) current and I(to,f) densities are significantly (P < 0.05) higher in cells from the apex than the base. In addition, I(to,f) and I(K,slow) densities are lower in cells isolated from the endocardial (Endo) than the epicardial (Epi) surface of the LV wall. Importantly, similar to LV apex cells, I(to,s) is not detected in RV, LV base, LV Epi or LV Endo myocytes. No measurable differences in K(+) current densities or properties are evident in RV or LV cells from adult male and female mice, although I(to,f), I(to,s), I(K,slow) and I(ss) densities are significantly (P < 0.01) higher, and action potential durations at 50% (APD(50)) are significantly (P < 0.05) shorter in male septum cells. Western blot analysis revealed that the expression levels of Kv4.2, Kv4.3, KChIP2, Kv1.5 and Kv2.1 are similar in male and female ventricles. In addition, consistent with the similarities in repolarizing Kv current densities, no measurable differences in ECG parameters, including corrected QT (QT(c)) intervals, are detected in telemetric recordings from adult male and female (C57BL6) mice.
Figures


References
-
- An WF, Bowlby MR, Betty M, Cao J, Li H-P, Mendoza G, Hinson JW, Mattsson KI, Strassle BW, Trimmer JS, Rhodes KJ. Modulation of A-type potassium channels by a family of calcium sensors. Nature. 2000;403:553–556. - PubMed
-
- Antzelevitch C, Dumaine R. Electrical heterogeneity in the heart: Physiological, pharmacological, and clinical implications. In: Page E, Fozzard HA, Solaro RJ, editors. The Handbook of Physiology, section 2, The Cardiovascular System, The Heart. Vol. 1. New York: Oxford University Press; 2002. pp. 654–692.
-
- Anumonwo J, Tallini YN, Vetter FJ, Jalife J. Action potential characteristics and arrhythmogenic properties of the cardiac conduction system of the murine heart. Circ Res. 2001;89:329–335. - PubMed
-
- Baker LC, London B, Choi BR, Koren G, Salama G. Enhanced dispersion of repolarization and refractoriness in transgenic mouse hearts promotes reentrant ventricular tachycardia. Circ Res. 2000;86:396–407. - PubMed
-
- Barry DM, Xu H, Schuessler RB, Nerbonne JM. Functional knockout of the transient outward current, long–QT syndrome, and cardiac remodeling in mice expressing a dominant- negative Kv4 alpha subunit. Circ Res. 1998;83:560–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

