Noninfectious X4 but not R5 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions inhibit humoral immune responses in human lymphoid tissue ex vivo
- PMID: 15194782
- PMCID: PMC421649
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.13.7061-7068.2004
Noninfectious X4 but not R5 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions inhibit humoral immune responses in human lymphoid tissue ex vivo
Abstract
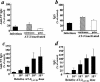
Ex vivo human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of human lymphoid tissue recapitulates some aspects of in vivo HIV-1 infection, including a severe depletion of CD4(+) T cells and suppression of humoral immune responses to recall antigens or to polyclonal stimuli. These effects are induced by infection with X4 HIV-1 variants, whereas infection with R5 variants results in only mild depletion of CD4(+) T cells and no suppression of immune responses. To study the mechanisms of suppression of immune responses in this ex vivo system, we used aldrithiol-2 (AT-2)-inactivated virions that have functional envelope glycoproteins but are not infectious and do not deplete CD4(+) T cells in human lymphoid tissues ex vivo. Nevertheless, AT-2-inactivated X4 (but not R5) HIV-1 virions, even with only a brief exposure, inhibit antibody responses in human lymphoid tissue ex vivo, similarly to infectious virus. This phenomenon is mediated by soluble immunosuppressive factor(s) secreted by tissue exposed to virus.
Figures
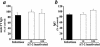



Similar articles
-
CD4(+) T-lymphocyte depletion in human lymphoid tissue ex vivo is not induced by noninfectious human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions.J Virol. 1998 Nov;72(11):9345-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.11.9345-9347.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9765486 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 pathogenesis differs in rectosigmoid and tonsillar tissues infected ex vivo with CCR5- and CXCR4-tropic HIV-1.AIDS. 2007 Jun 19;21(10):1263-72. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3281864667. AIDS. 2007. PMID: 17545702
-
CXCR4 utilization is sufficient to trigger CD4+ T cell depletion in HIV-1-infected human lymphoid tissue.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jan 19;96(2):663-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.2.663. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 9892690 Free PMC article.
-
Sites, mechanism of action and lack of reversibility of primate lentivirus inactivation by preferential covalent modification of virion internal proteins.Curr Mol Med. 2003 May;3(3):265-72. doi: 10.2174/1566524033479889. Curr Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 12699362 Review.
-
The role of viral coreceptors and enhanced macrophage tropism in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 disease progression.Sex Health. 2004;1(1):23-34. doi: 10.1071/sh03006. Sex Health. 2004. PMID: 16335478 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune suppression of human lymphoid tissues and cells in rotating suspension culture and onboard the International Space Station.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2009 Dec;45(10):622-32. doi: 10.1007/s11626-009-9225-2. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2009. PMID: 19609626 Free PMC article.
-
HIV inhibits CD4+ T-cell proliferation by inducing indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in plasmacytoid dendritic cells.Blood. 2007 Apr 15;109(8):3351-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-034785. Epub 2006 Dec 7. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17158233 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Abnormal activation and cytokine spectra in lymph nodes of people chronically infected with HIV-1.Blood. 2007 May 15;109(10):4272-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-11-055764. Epub 2007 Feb 8. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17289812 Free PMC article.
-
Fusion-induced apoptosis contributes to thymocyte depletion by a pathogenic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope in the human thymus.J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(22):11019-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01382-06. Epub 2006 Sep 6. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16956934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amadori, A., G. P. Faulkner-Valle, A. De Rossi, P. Zanovello, D. Collavo, and L. Chieco-Bianchi. 1988. HIV-mediated immunodepression: in vitro inhibition of T-lymphocyte proliferative response by ultraviolet-inactivated virus. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 46:37-54. - PubMed
-
- Arthur, L. O., J. W. Bess, Jr., E. N. Chertova, J. L. Rossio, M. T. Esser, R. E. Benveniste, L. E. Henderson, and J. D. Lifson. 1998. Chemical inactivation of retroviral infectivity by targeting nucleocapsid protein zinc fingers: a candidate SIV vaccine. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 14(Suppl. 3):S311-S319. - PubMed
-
- Barbi, M., M. R. Biffi, S. Binda, M. Clerici-Schoeller, G. Ferraris, C. Luraschi, P. Masella, P. Mazzoni, A. Pozzi, F. Pregliasco, et al. 1992. Immunization in children with HIV seropositivity at birth: antibody response to polio vaccine and tetanus toxoid. AIDS 6:1465-1469. - PubMed
-
- Berger, E. A., R. W. Doms, E. M. Fenyo, B. T. Korber, D. R. Littman, J. P. Moore, Q. J. Sattentau, H. Schuitemaker, J. Sodroski, and R. A. Weiss. 1998. A new classification for HIV-1. Nature 391:240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

