Toll-like receptor (TLR) expression and TLR-mediated cytokine/chemokine production by human uterine epithelial cells
- PMID: 15196211
- PMCID: PMC1782499
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01898.x
Toll-like receptor (TLR) expression and TLR-mediated cytokine/chemokine production by human uterine epithelial cells
Abstract
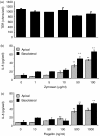
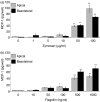
The objective of this study was to examine the expression of toll-like receptors (TLRs) by the uterine epithelial cell line ECC-1 and to determine if stimulation of the expressed TLRs induces changes in cytokine and/or chemokine secretion. The expression of TLR1 to TLR9 by ECC-1 cells was demonstrated by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, with only TLR10 not being expressed. Stimulation of ECC-1 cells using agonists to TLR2, TLR4 and TLR5 induced the expression of the chemokines interleukin-8 (IL-8) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), as well as the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6, and occurred in a dose-dependent manner. In response to zymosan and flagellin, pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMP) that are recognized by TLR2 and TLR5 respectively, ECC-1 cells secreted significantly more IL-8, MCP-1 and IL-6 than in response to other TLR agonists. In contrast, agonists to TLR3, TLR7, and TLR9 had no effect on the secretion of the 13 cytokines or chemokines analysed. These results indicate that uterine epithelial cells are important sentinels of the innate immune system. Further it indicates that all but one of the known TLRs are expressed by ECC-1 cells and that stimulation through specific TLRs mediates changes in the expression of key chemokines and pro-inflammatory cytokines that aid in the defence of the uterus against potential pathogens.
Figures

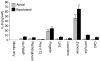
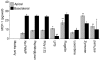
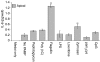
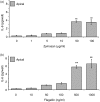
References
-
- Quayle AJ. The innate and early immune response to pathogen challenge in the female genital tract and the pivotal role of epithelial cells. J Reprod Immunol. 2002;57:61–79. - PubMed
-
- King AE, Critchley HO, Kelly RW. Presence of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor in human endometrium and first trimester decidua suggests an antibacterial protective role. Mol Hum Reprod. 2000;6:191–6. - PubMed
-
- Fleming DC, King AE, Williams AR, Critchley HO, Kelly RW. Hormonal contraception can suppress natural antimicrobial gene transcription in human endometrium. Fertil Steril. 2003;79:856–63. - PubMed
-
- King AE, Fleming DC, Critchley HO, Kelly RW. Differential expression of the natural antimicrobials, beta-defensins 3 and 4, in human endometrium. J Reprod Immunol. 2003;59:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Arici A, Head JR, MacDonald PC, Casey ML. Regulation of interleukin-8 gene expression in human endometrial cells in culture. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1993;94:195–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
